Avdoralimab (Anti-C5aR1 mAb) Versus Placebo in Patients With Severe COVID-19: Results From a Randomized Controlled Trial (FOR COVID Elimination [FORCE])
- PMID: 36218354
- PMCID: PMC9674430
- DOI: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000005683
Avdoralimab (Anti-C5aR1 mAb) Versus Placebo in Patients With Severe COVID-19: Results From a Randomized Controlled Trial (FOR COVID Elimination [FORCE])
Abstract
Objectives: Severe COVID-19 is associated with exaggerated complement activation. We assessed the efficacy and safety of avdoralimab (an anti-C5aR1 mAb) in severe COVID-19.
Design: FOR COVID Elimination (FORCE) was a double-blind, placebo-controlled study.
Setting: Twelve clinical sites in France (ICU and general hospitals).
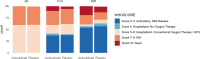
Patients: Patients receiving greater than or equal to 5 L oxygen/min to maintain Sp o2 greater than 93% (World Health Organization scale ≥ 5). Patients received conventional oxygen therapy or high-flow oxygen (HFO)/noninvasive ventilation (NIV) in cohort 1; HFO, NIV, or invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV) in cohort 2; and IMV in cohort 3.
Interventions: Patients were randomly assigned, in a 1:1 ratio, to receive avdoralimab or placebo. The primary outcome was clinical status on the World Health Organization ordinal scale at days 14 and 28 for cohorts 1 and 3, and the number of ventilator-free days at day 28 (VFD28) for cohort 2.
Measurements and main results: We randomized 207 patients: 99 in cohort 1, 49 in cohort 2, and 59 in cohort 3. During hospitalization, 95% of patients received glucocorticoids. Avdoralimab did not improve World Health Organization clinical scale score on days 14 and 28 (between-group difference on day 28 of -0.26 (95% CI, -1.2 to 0.7; p = 0.7) in cohort 1 and -0.28 (95% CI, -1.8 to 1.2; p = 0.6) in cohort 3). Avdoralimab did not improve VFD28 in cohort 2 (between-group difference of -6.3 (95% CI, -13.2 to 0.7; p = 0.96) or secondary outcomes in any cohort. No subgroup of interest was identified.
Conclusions: In this randomized trial in hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia, avdoralimab did not significantly improve clinical status at days 14 and 28 (funded by Innate Pharma, ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT04371367).
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the Society of Critical Care Medicine and Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Carvelli received support for article research from Innate Pharma. Drs. Carvelli, Allardet-Servent, Barbar, Desgrouas, Camou, Piperoglou, Viotti, Boyer-Chammard, Lacombe, Le Dault, Schleinitz, and Vivier disclosed the off-label product use of avdoralimab. Dr. Guervilly received funding from Xenios FMC. Dr. Demaria’s institution received funding from BPI. Drs. Demaria, Karakunnel, Fares, Batista, Boyer-Chammard, and Vivier received funding from innate pharma. Drs. Demaria, Karakunnel, Fares, Batista, Rotolo, Viotti, Boyer-Chammard, and Vivier disclosed that they are employees of Innate Pharma. Dr. Karakunnel received funding from Primevax Precision Biologics. Dr. Rotolo received funding from Sanofi. Dr. Viotti disclosed work for hire. Dr. Lacombe received funding from MSD, Gilead, Janssen, and ViiV Healthcare. Dr. Vivier disclosed that he is a cofounder, shareholder, and employee of Innate Pharma and that his spouse is a shareholder of Innate Pharma. The remaining authors have disclosed that they do not have any potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

Comment in
-
Maintaining Momentum in Clinical Trials for Respiratory Viruses.Crit Care Med. 2022 Dec 1;50(12):1840-1842. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000005689. Epub 2022 Nov 17. Crit Care Med. 2022. PMID: 36394404 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
C5a-C5aR1 Axis Blockade in Patients With Severe COVID-19: Contrasting Results of PANAMO and FORCE.Crit Care Med. 2023 May 1;51(5):e129-e130. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000005796. Epub 2023 Apr 13. Crit Care Med. 2023. PMID: 37052450 No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization: WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available at: https://covid19.who.int. Accessed September 28, 2022

