Incidence of Pediatric Celiac Disease Varies by Region
- PMID: 36219178
- PMCID: PMC9991947
- DOI: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000002056
Incidence of Pediatric Celiac Disease Varies by Region
Abstract
Introduction: The Environmental Determinants of Diabetes in the Young study follows an HLA risk selected birth cohort for celiac disease (CD) development using a uniform protocol. Children under investigation come from 6 different regions within Europe and the United States. Our aim was to identify regional differences in CD autoimmunity and CD cumulative incidence for children born between 2004 and 2010.
Methods: Children (n = 6,628) with DQ2.5 and/or DQ8.1 were enrolled prospectively from birth in Georgia, Washington, Colorado, Finland, Germany, and Sweden. Children underwent periodic study screening for tissue transglutaminase antibodies and then CD evaluation per clinical care. Population-specific estimates were calculated by weighting the study-specific cumulative incidence with the population-specific haplogenotype frequencies obtained from large stem cell registries from each site.
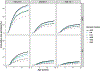
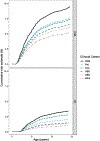
Results: Individual haplogenotype risks for CD autoimmunity and CD varied by region and affected the cumulative incidence within that region. The CD incidence by age 10 years was highest in Swedish children at 3%. Within the United States, the incidence by age 10 years in Colorado was 2.4%. In the model adjusted for HLA, sex, and family history, Colorado children had a 2.5-fold higher risk of CD compared to Washington. Likewise, Swedish children had a 1.4-fold and 1.8-fold higher risk of CD compared with those in Finland and Germany, respectively.
Discussion: There is high regional variability in cumulative incidence of CD, which suggests differential environmental, genetic, and epigenetic influences even within the United States. The overall high incidence warrants a low threshold for screening and further research on region-specific CD triggers.
Copyright © 2022 by The American College of Gastroenterology.
Figures
References
-
- King JA, et al., Incidence of Celiac Disease Is Increasing Over Time: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol, 2020. 115(4): p. 507–525. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 DK063821/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063863/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002535/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN267200700014C/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK128847/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063790/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000064/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN267200700014C/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063829/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063865/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK095300/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063861/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063829/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063821/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK117483/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK112243/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK124166/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063861/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063865/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063863/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK106955/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK100238/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

