Nuclear mRNA metabolism drives selective basket assembly on a subset of nuclear pore complexes in budding yeast
- PMID: 36220102
- PMCID: PMC10300651
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.09.019
Nuclear mRNA metabolism drives selective basket assembly on a subset of nuclear pore complexes in budding yeast
Abstract
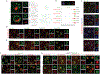
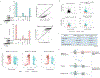
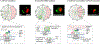
To determine which transcripts should reach the cytoplasm for translation, eukaryotic cells have established mechanisms to regulate selective mRNA export through the nuclear pore complex (NPC). The nuclear basket, a substructure of the NPC protruding into the nucleoplasm, is thought to function as a stable platform where mRNA-protein complexes (mRNPs) are rearranged and undergo quality control prior to export, ensuring that only mature mRNAs reach the cytoplasm. Here, we use proteomic, genetic, live-cell, and single-molecule resolution microscopy approaches in budding yeast to demonstrate that basket formation is dependent on RNA polymerase II transcription and subsequent mRNP processing. We further show that while all NPCs can bind Mlp1, baskets assemble only on a subset of nucleoplasmic NPCs, and these basket-containing NPCs associate a distinct protein and RNA interactome. Taken together, our data point toward NPC heterogeneity and an RNA-dependent mechanism for functionalization of NPCs in budding yeast through nuclear basket assembly.
Keywords: Mlp1; NPC heterogeneity; basket accessory interactome; mRNA export; mRNA processing; nuclear basket; nuclear compartmentalization; nuclear pore complex; nucleolus; poly(A) transcripts.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
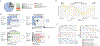
References
-
- Aguilar L-C, Paul B, Reiter T, Gendron L, Rajan AAN, Montpetit R, Trahan C, Pechmann S, Oeffinger M, and Montpetit B (2020). Altered rRNA processing disrupts nuclear RNA homeostasis via competition for the poly(A)-binding protein Nab2. Nucleic Acids Res 48, 11675–11694. 10.1093/nar/gkaa964. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

