Changes in cardiorespiratory function and fatigue following 12 weeks of exercise training in women with systemic lupus erythematosus: a pilot study
- PMID: 36220328
- PMCID: PMC9557301
- DOI: 10.1136/lupus-2022-000778
Changes in cardiorespiratory function and fatigue following 12 weeks of exercise training in women with systemic lupus erythematosus: a pilot study
Abstract
Objective: In patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), fatigue is a debilitating symptom with poorly understood pathophysiology. Cardiorespiratory dysfunction has been hypothesised as a contributor to SLE-fatigue. The purpose of this exploratory study was to examine changes in cardiorespiratory function, following an exercise training programme in women with SLE, together with patient reported outcomes and other pathophysiological measures that may underlie SLE-fatigue.
Methods: Sixteen women with SLE and fatigue (Fatigue Severity Scale (FSS) ≥3) were enrolled in a supervised aerobic exercise training programme of vigorous intensity. The primary outcome was time to reach anaerobic threshold (AT-Time) during a cardiopulmonary exercise test (CPET). Secondary outcomes included changes in the 10-minute walk test (10MWT), FSS scores and the Patient Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS-57) survey. Mitochondrial function was assessed by the oxygen consumption rate (OCR)/extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) metabolic potential ratio.
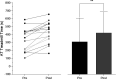
Results: Following 12 weeks of exercise training, AT-Time increased by 93±82 (mean±SD) s (p<0.001), 10MWT increased by 84±66 m (p<0.001) and peak oxygen uptake (VO2) increased by 1.4±2.0 mL/kg/min (p=0.013). There were improvements in FSS score (-1.4±1.0, p<0.0001) and in most of the PROMIS-57 domains. The decrease in FSS scores correlated with an increase in the OCR/ECAR ratio (Pearson's correlation r=-0.59, p=0.03). A subset of subjects (9/15) had significant reduction in their Interferon Stimulated Genes (ISG) (p=0.007) accompanied by a significant increase in the OCR/ECAR ratio (p=0.013).
Conclusions: Cardiorespiratory function was improved in concomitance with reductions in fatigue following a 12-week aerobic exercise programme. The reduction in fatigue scores correlated with improvements in mitochondrial function.
Keywords: exercise therapy; lupus erythematosus, systemic; quality of lIfe.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Wasserman K, Hansen JE, Sue DY. Principles of exercise testing and interpretation: including pathophysiology and clinical applications. 4th. Baltimore, MD: Lippincott Williams & Williams, 2005.
-
- Hays RD, Spritzer KL, Fries JF, et al. . Responsiveness and minimally important difference for the patient-reported outcomes measurement information system (PROMIS) 20-item physical functioning short form in a prospective observational study of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2015;74:104–7. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204053 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
