Cancer-associated Fibroblasts Communicate with Breast Tumor Cells Through Extracellular Vesicles in Tumor Development
- PMID: 36222020
- PMCID: PMC9558853
- DOI: 10.1177/15330338221131647
Cancer-associated Fibroblasts Communicate with Breast Tumor Cells Through Extracellular Vesicles in Tumor Development
Abstract
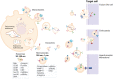
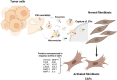
Breast cancer is the leading cause of cancer death among women worldwide. In solid tumors, the microenvironment plays a critical role in tumor development, and it has been described a communication between the different cell types that conform the stroma, including fibroblasts, pericytes, adipocytes, immune cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts. Intercellular communication is bidirectional, complex, multifactorial and is mediated by the secretion of molecules and extracellular vesicles. The extracellular vesicles are vesicles limited by two membranes that are secreted by normal and cancer cells into the extracellular space. Extracellular vesicle cargo is complex and includes proteins, miRNAs, DNA and lipids, and their composition is specific to their parent cells. Extracellular vesicles are taken up for neighboring or distant cells. Particularly, extracellular vesicles from breast cancer cells are taken up for fibroblasts and it induces the activation of fibroblasts into cancer-associated fibroblasts. Interestingly, cancer associated fibroblasts release extracellular vesicles that are taken up for breast cancer cells and promote migration, invasion, proliferation, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, changes in metabolism, chemoresistance, evasion of immune system and remodeling of extracellular matrix. In addition, the enrichment of specific cargos in extracellular vesicles of breast cancer patients has been suggested to be used as biomarkers of the disease. Here we review the current literature about the intercommunication between tumor cells and cancer associated fibroblasts through extracellular vesicles in breast cancer.
Keywords: breast cancer; cancer-associated fibroblasts; extracellular vesicles; microenvironment; stroma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Role of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts and Extracellular Vesicles in Tumorigenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 17;21(18):6837. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186837. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32957712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer associated-fibroblast-derived exosomes in cancer progression.Mol Cancer. 2021 Dec 1;20(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01463-y. Mol Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34852849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Secretion rates and protein composition of extracellular vesicles released by cancer-associated fibroblasts after radiation.J Radiat Res. 2021 May 12;62(3):401-413. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrab018. J Radiat Res. 2021. PMID: 33899109 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicles as a novel approach for breast cancer therapeutics.Cancer Lett. 2023 Feb 28;555:216036. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2022.216036. Epub 2022 Dec 12. Cancer Lett. 2023. PMID: 36521658 Review.
-
MicroRNA-370-3p shuttled by breast cancer cell-derived extracellular vesicles induces fibroblast activation through the CYLD/Nf-κB axis to promote breast cancer progression.FASEB J. 2021 Mar;35(3):e21383. doi: 10.1096/fj.202001430RR. FASEB J. 2021. PMID: 33629796
Cited by
-
Endosialin in Cancer: Expression Patterns, Mechanistic Insights, and Therapeutic Approaches.Theranostics. 2024 Jan 1;14(1):379-391. doi: 10.7150/thno.89495. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 38164138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the multifaceted role of direct interaction between cancer cells and fibroblasts in cancer progression.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 May 28;11:1379971. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1379971. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38863965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IRF5 suppresses metastasis through the regulation of tumor-derived extracellular vesicles and pre-metastatic niche formation.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 5;14(1):15557. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66168-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38969706 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Extracellular Vesicles on Lung Stromal Cells during Breast Cancer Metastasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 22;24(14):11801. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411801. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modeling the role of urokinase plasminogen activator, uPA, and circulating Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts (cCAFS) in breast cancer cell extravasation.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 17:2025.06.11.659108. doi: 10.1101/2025.06.11.659108. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40667030 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

