Chemical tools to track and perturb the expression of sialic acid and fucose monosaccharides
- PMID: 36222364
- PMCID: PMC9623448
- DOI: 10.1039/d2cc04275d
Chemical tools to track and perturb the expression of sialic acid and fucose monosaccharides
Abstract
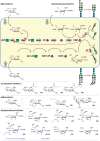
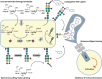
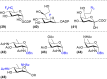
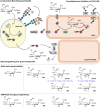
The biosynthesis of glycans is a highly conserved biological process and found in all domains of life. The expression of cell surface glycans is increasingly recognized as a target for therapeutic intervention given the role of glycans in major pathologies such as cancer and microbial infection. Herein, we summarize our contributions to the development of unnatural monosaccharide derivatives to infiltrate and alter the expression of both mammalian and bacterial glycans and their therapeutic application.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Synthesis of a Highly Branched Nonasaccharide Chlorella Virus N-Glycan Using a "Counterclockwise" Assembly Approach.Org Lett. 2020 Oct 2;22(19):7645-7649. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.0c02839. Epub 2020 Sep 17. Org Lett. 2020. PMID: 32940477
-
Terminal monosaccharide expression on amniotic glycoproteins as biomarkers of fetus maturity.Biochem Soc Trans. 2011 Jan;39(1):344-8. doi: 10.1042/BST0390344. Biochem Soc Trans. 2011. PMID: 21265801 Review.
-
L1CAM from human melanoma carries a novel type of N-glycan with Galβ1-4Galβ1- motif. Involvement of N-linked glycans in migratory and invasive behaviour of melanoma cells.Glycoconj J. 2013 Apr;30(3):205-25. doi: 10.1007/s10719-012-9374-5. Epub 2012 Apr 29. Glycoconj J. 2013. PMID: 22544341 Free PMC article.
-
Statistical analysis of the Bacterial Carbohydrate Structure Data Base (BCSDB): characteristics and diversity of bacterial carbohydrates in comparison with mammalian glycans.BMC Struct Biol. 2008 Aug 11;8:35. doi: 10.1186/1472-6807-8-35. BMC Struct Biol. 2008. PMID: 18694500 Free PMC article.
-
Increasing the sialylation of therapeutic glycoproteins: the potential of the sialic acid biosynthetic pathway.J Pharm Sci. 2009 Oct;98(10):3499-508. doi: 10.1002/jps.21684. J Pharm Sci. 2009. PMID: 19199295 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting aberrant sialylation and fucosylation in prostate cancer cells using potent metabolic inhibitors.Glycobiology. 2023 Dec 30;33(12):1155-1171. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwad085. Glycobiology. 2023. PMID: 37847613 Free PMC article.
-
UV light-induced spatial loss of sialic acid capping using a photoactivatable sialyltransferase inhibitor.RSC Chem Biol. 2023 May 25;4(7):506-511. doi: 10.1039/d3cb00006k. eCollection 2023 Jul 5. RSC Chem Biol. 2023. PMID: 37415865 Free PMC article.
-
FUT8 Is a Critical Driver of Prostate Tumour Growth and Can Be Targeted Using Fucosylation Inhibitors.Cancer Med. 2025 May;14(10):e70959. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70959. Cancer Med. 2025. PMID: 40387385 Free PMC article.
-
Realizing the promise of 'La Dolce Vita' via chemical biology: glycan-motif editing of sLeX for precision cancer therapeutics.FEBS J. 2025 Jul;292(14):3616-3628. doi: 10.1111/febs.70079. Epub 2025 Mar 27. FEBS J. 2025. PMID: 40146612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monitoring host-pathogen interactions using chemical proteomics.RSC Chem Biol. 2023 Nov 10;5(2):73-89. doi: 10.1039/d3cb00135k. eCollection 2024 Feb 7. RSC Chem Biol. 2023. PMID: 38333198 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Prestegard J. H., Essentials of glycobiology, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, NY, United States, 3rd edn, 2017
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

