PRC2-Mediated Epigenetic Suppression of Type I IFN-STAT2 Signaling Impairs Antitumor Immunity in Luminal Breast Cancer
- PMID: 36222718
- PMCID: PMC9772098
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-22-0736
PRC2-Mediated Epigenetic Suppression of Type I IFN-STAT2 Signaling Impairs Antitumor Immunity in Luminal Breast Cancer
Abstract
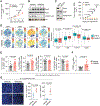
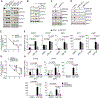
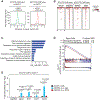
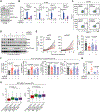
The immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment in some cancer types, such as luminal breast cancer, supports tumor growth and limits therapeutic efficacy. Identifying approaches to induce an immunostimulatory environment could help improve cancer treatment. Here, we demonstrate that inhibition of cancer-intrinsic EZH2 promotes antitumor immunity in estrogen receptor α-positive (ERα+) breast cancer. EZH2 is a component of the polycomb-repressive complex 2 (PRC2) complex, which catalyzes trimethylation of histone H3 at lysine 27 (H3K27me3). A 53-gene PRC2 activity signature was closely associated with the immune responses of ERα+ breast cancer cells. The stimulatory effects of EZH2 inhibition on immune surveillance required specific activation of type I IFN signaling. Integrative analysis of PRC2-repressed genes and genome-wide H3K27me3 landscape revealed that type I IFN ligands are epigenetically silenced by H3K27me3. Notably, the transcription factor STAT2, but not STAT1, mediated the immunostimulatory functions of type I IFN signaling. Following EZH2 inhibition, STAT2 was recruited to the promoters of IFN-stimulated genes even in the absence of the cytokines, suggesting the formation of an autocrine IFN-STAT2 axis. In patients with luminal breast cancer, high levels of EZH2 and low levels of STAT2 were associated with the worst antitumor immune responses. Collectively, this work paves the way for the development of an effective therapeutic strategy that may reverse immunosuppression in cancer.
Significance: Inhibition of EZH2 activates a type I IFN-STAT2 signaling axis and provides a therapeutic strategy to stimulate antitumor immunity and therapy responsiveness in immunologically cold luminal breast cancer.
©2022 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Global H3K27 trimethylation and EZH2 abundance in breast tumor subtypes.Mol Oncol. 2012 Oct;6(5):494-506. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2012.06.002. Epub 2012 Jun 20. Mol Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22766277 Free PMC article.
-
p38-mediated phosphorylation at T367 induces EZH2 cytoplasmic localization to promote breast cancer metastasis.Nat Commun. 2018 Jul 18;9(1):2801. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05078-8. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30022044 Free PMC article.
-
Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 in Oncology.Cancer Treat Res. 2023;190:273-320. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-45654-1_9. Cancer Treat Res. 2023. PMID: 38113005
-
Noncanonical Functions of the Polycomb Group Protein EZH2 in Breast Cancer.Am J Pathol. 2021 May;191(5):774-783. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2021.01.013. Epub 2021 Feb 6. Am J Pathol. 2021. PMID: 33556366 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The roles of EZH2 in cancer and its inhibitors.Med Oncol. 2023 May 6;40(6):167. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-02025-6. Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37148376 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lysine methylation modifications in tumor immunomodulation and immunotherapy: regulatory mechanisms and perspectives.Biomark Res. 2024 Jul 30;12(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s40364-024-00621-w. Biomark Res. 2024. PMID: 39080807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Regulation of Stromal and Immune Cells and Therapeutic Targets in the Tumor Microenvironment.Biomolecules. 2025 Jan 6;15(1):71. doi: 10.3390/biom15010071. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 39858465 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting polycomb repressor complex 2-mediated bivalent promoter epigenetic silencing of secreted frizzled-related protein 1 inhibits cholangiocarcinoma progression.Clin Transl Med. 2023 Dec;13(12):e1502. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1502. Clin Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 38050190 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular senescence-related genes: predicting prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2023 Oct 18;23(1):1001. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11288-1. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37853322 Free PMC article.
-
Evolving cognition of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway: autoimmune disorders and cancer.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 May 19;8(1):204. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01468-7. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 37208335 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cao R, Zhang Y. SUZ12 is required for both the histone methyltransferase activity and the silencing function of the EED-EZH2 complex. Mol Cell 2004;15:57–67 - PubMed
-
- Cao R, Wang L, Wang H, Xia L, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, et al. Role of histone H3 lysine 27 methylation in Polycomb-group silencing. Science 2002;298:1039–43 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

