Angiotensin converting enzyme 2 level and its significance in COVID-19 and other diseases patients
- PMID: 36222740
- PMCID: PMC9874405
- DOI: 10.1111/eci.13891
Angiotensin converting enzyme 2 level and its significance in COVID-19 and other diseases patients
Abstract
Background: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) expressions and its modulation are of great interest as being a key receptor for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV2) and the protective arm of the rennin-angiotensin axis, maintaining cardiovascular homeostasis. However, ACE2 expressions and their modulation in the healthy and disease background are yet to be explored.
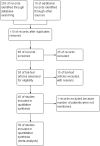
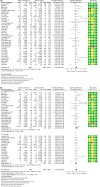
Method: We performed a meta-analysis, extracting the data for ACE2 expression in human subjects with various diseases, including SARS-CoV2 infection without or with co-morbidity. The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines were followed. Out of 203 studies, 39 met the inclusion criteria with SARS-CoV2 patients without co-morbidity, SARS-CoV2 patients with co-morbidity, cardiovascular (CVD) patients, diabetes patients, kidney disorders patients, pulmonary disease patients, and other viral infections patients.
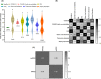
Results: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 expression was significantly increased in all diseases. There was an elevated level of ACE2, especially membrane-bound ACE2, in COVID-19 patients compared to healthy controls. A statistically significant increase in ACE2 expression was observed in CVD patients and patients with other viral diseases compared to healthy subjects. Moreover, subgroup analysis of ACE2 expression as soluble and membrane-bound ACE2 revealed a remarkable increase in membrane-bound ACE2 in CVD patients, patients with viral infection compared to soluble ACE2 and pooled standard mean difference (SMD) with the random-effects model was 0.37 and 2.23 respectively.
Conclusion: It was observed that utilizing the ACE2 by SARS-CoV2 for its entry and its consequence leads to several complications. So there is a need to investigate the underlying mechanism along with novel therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: RAS; SARS-CoV2; cardiovascular diseases; membrane-bound ACE2; soluble ACE2.
© 2022 Stichting European Society for Clinical Investigation Journal Foundation. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Testing the efficacy and safety of BIO101, for the prevention of respiratory deterioration, in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia (COVA study): a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Jan 11;22(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04998-5. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33430924 Free PMC article.
-
Drugs acting on renin angiotensin system and use in ill patients with COVID-19.Therapie. 2020 Jul-Aug;75(4):319-325. doi: 10.1016/j.therap.2020.05.009. Epub 2020 May 20. Therapie. 2020. PMID: 32553503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and COVID-19 infection.Ann Endocrinol (Paris). 2020 Jun;81(2-3):63-67. doi: 10.1016/j.ando.2020.04.005. Epub 2020 Apr 21. Ann Endocrinol (Paris). 2020. PMID: 32370986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Role of ACE2 in COVID-19].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2022;157(2):115-118. doi: 10.1254/fpj.21104. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2022. PMID: 35228442 Japanese.
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), SARS-CoV-2 and the pathophysiology of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).J Pathol. 2020 Jul;251(3):228-248. doi: 10.1002/path.5471. Epub 2020 Jun 10. J Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32418199 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SARS-CoV-2 infection and its effects on the endocrine system.Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023 Jul;37(4):101761. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2023.101761. Epub 2023 Mar 5. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023. PMID: 36907787 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Banu N, Surendra S, Riera L, Riera A. Since January 2020, Elsevier has created a COVID‐19 resource centre with free information in English and Mandarin on the novel coronavirus COVID‐19. The COVID‐19 resource centre is hosted on Elsevier Connect, the company's public news and information. 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

