Upper cortical layer-driven network impairment in schizophrenia
- PMID: 36223459
- PMCID: PMC9555788
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abn8367
Upper cortical layer-driven network impairment in schizophrenia
Abstract
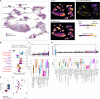
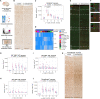
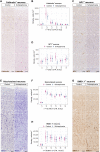
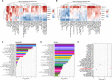
Schizophrenia is one of the most widespread and complex mental disorders. To characterize the impact of schizophrenia, we performed single-nucleus RNA sequencing (snRNA-seq) of >220,000 neurons from the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of patients with schizophrenia and matched controls. In addition, >115,000 neurons were analyzed topographically by immunohistochemistry. Compositional analysis of snRNA-seq data revealed a reduction in abundance of GABAergic neurons and a concomitant increase in principal neurons, most pronounced for upper cortical layer subtypes, which was substantiated by histological analysis. Many neuronal subtypes showed extensive transcriptomic changes, the most marked in upper-layer GABAergic neurons, including down-regulation in energy metabolism and up-regulation in neurotransmission. Transcription factor network analysis demonstrated a developmental origin of transcriptomic changes. Last, Visium spatial transcriptomics further corroborated upper-layer neuron vulnerability in schizophrenia. Overall, our results point toward general network impairment within upper cortical layers as a core substrate associated with schizophrenia symptomatology.
Figures



References
-
- GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators , Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 Diseases and Injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 392, 1789–1858 (2018). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Millan M. J., Andrieux A., Bartzokis G., Cadenhead K., Dazzan P., Fusar-Poli P., Gallinat J., Giedd J., Grayson D. R., Heinrichs M., Kahn R., Krebs M. O., Leboyer M., Lewis D., Marin O., Marin P., Meyer-Lindenberg A., McGorry P., McGuire P., Owen M. J., Patterson P., Sawa A., Spedding M., Uhlhaas P., Vaccarino F., Wahlestedt C., Weinberger D., Altering the course of schizophrenia: Progress and perspectives. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 15, 485–515 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Lewis D. A., Hashimoto T., Volk D. W., Cortical inhibitory neurons and schizophrenia. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 6, 312–324 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Skene N. G., Bryois J., Bakken T. E., Breen G., Crowley J. J., Gaspar H. A., Giusti-Rodriguez P., Hodge R. D., Miller J. A., Muñoz-Manchado A. B., O’Donovan M. C., Owen M. J., Pardiñas A. F., Ryge J., Walters J. T. R., Linnarsson S., Lein E. S.; Major Depressive Disorder Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium, Sullivan P. F., Hjerling-Leffler J., Genetic identification of brain cell types underlying schizophrenia. Nat. Genet. 50, 825–833 (2018). - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

