Helheim Glacier ice velocity variability responds to runoff and terminus position change at different timescales
- PMID: 36224175
- PMCID: PMC9556534
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-33292-y
Helheim Glacier ice velocity variability responds to runoff and terminus position change at different timescales
Abstract
The Greenland Ice Sheet discharges ice to the ocean through hundreds of outlet glaciers. Recent acceleration of Greenland outlet glaciers has been linked to both oceanic and atmospheric drivers. Here, we leverage temporally dense observations, regional climate model output, and newly developed time series analysis tools to assess the most important forcings causing ice flow variability at one of the largest Greenland outlet glaciers, Helheim Glacier, from 2009 to 2017. We find that ice speed correlates most strongly with catchment-integrated runoff at seasonal to interannual scales, while multi-annual flow variability correlates most strongly with multi-annual terminus variability. The disparate time scales and the influence of subglacial topography on Helheim Glacier's dynamics highlight different regimes that can inform modeling and forecasting of its future. Notably, our results suggest that the recent terminus history observed at Helheim is a response to, rather than the cause of, upstream changes.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
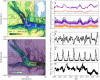
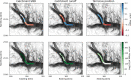
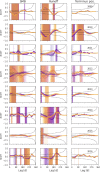

References
-
- Rignot E, Velicogna I, van den Broeke MR, Monaghan A, Lenaerts JTM. Acceleration of the contribution of the Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets to sea level rise. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011;38:L05503. doi: 10.1029/2011GL046583. - DOI
-
- Bevan SL, Luckman AJ, Murray T. Glacier dynamics over the last quarter of a century at Helheim, Kangerdlugssuaq and 14 other major Greenland outlet glaciers. Cryosphere. 2012;6:923–937. doi: 10.5194/tc-6-923-2012. - DOI
-
- Murray T, et al. Ocean regulation hypothesis for glacier dynamics in southeast Greenland and implications for ice sheet mass changes. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2010;115:F03026. doi: 10.1029/2009JF001522. - DOI
-
- Rignot E, Fenty I, Menemenlis D, Xu Y. Spreading of warm ocean waters around Greenland as a possible cause for glacier acceleration. Ann. Glaciol. 2012;53:257–266. doi: 10.3189/2012AoG60A136. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

