Immunogenicity of MultiTEP platform technology-based Tau vaccine in non-human primates
- PMID: 36224191
- PMCID: PMC9556597
- DOI: 10.1038/s41541-022-00544-3
Immunogenicity of MultiTEP platform technology-based Tau vaccine in non-human primates
Abstract
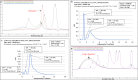
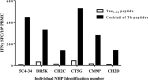
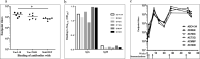
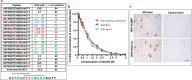
Pathological forms of Tau protein are directly associated with neurodegeneration and correlate with Alzheimer's Disease (AD) symptoms, progression, and severity. Previously, using various mouse models of Tauopathies and AD, we have demonstrated the immunogenicity and efficacy of the MultiTEP-based adjuvanted vaccine targeting the phosphatase activating domain (PAD) of Tau, AV-1980R/A. Here, we analyzed its immunogenicity in non-human primates (NHP), the closest phylogenic relatives to humans with a similar immune system, to initiate the transition of this vaccine into clinical trials. We have demonstrated that AV-1980R/A is highly immunogenic in these NHPs, activating a broad but unique to each monkey repertoire of MultiTEP-specific T helper (Th) cells that, in turn, activate B cells specific to PAD. The resulting anti-PAD IgG antibodies recognize pathological Tau tangles and Tau-positive neuritis in AD case brain sections with no staining in control non-AD cases. These published data and efficacy results support the AV-1980R/A vaccine progression to first-in-human clinical trials.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
N.P. is a founder of Vaxine, which developed the AdvaxCpG adjuvant. The authors declare no financial, commercial, or nonfinancial conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Alzheimer's disease Advax(CpG)- adjuvanted MultiTEP-based dual and single vaccines induce high-titer antibodies against various forms of tau and Aβ pathological molecules.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 1;6:28912. doi: 10.1038/srep28912. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27363809 Free PMC article.
-
A MultiTEP platform-based epitope vaccine targeting the phosphatase activating domain (PAD) of tau: therapeutic efficacy in PS19 mice.Sci Rep. 2019 Oct 29;9(1):15455. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-51809-2. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31664089 Free PMC article.
-
Active immunization with tau epitope in a mouse model of tauopathy induced strong antibody response together with improvement in short memory and pSer396-tau pathology.Neurobiol Dis. 2020 Feb;134:104636. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2019.104636. Epub 2019 Oct 17. Neurobiol Dis. 2020. PMID: 31629891 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and preclinical evaluation of the cGMP grade DNA based vaccine, AV-1959D to enter the first-in-human clinical trials.Neurobiol Dis. 2020 Jun;139:104823. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2020.104823. Epub 2020 Feb 28. Neurobiol Dis. 2020. PMID: 32119976 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tau Interacting Proteins: Gaining Insight into the Roles of Tau in Health and Disease.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1184:145-166. doi: 10.1007/978-981-32-9358-8_13. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 32096036 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Vaccine against Pathological Pyroglutamate-Modified Amyloid Beta for Prevention of Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 6;24(12):9797. doi: 10.3390/ijms24129797. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37372944 Free PMC article.
-
Advax-CpG55.2-adjuvanted monovalent or trivalent SARS-CoV-2 recombinant spike protein vaccine protects hamsters against heterologous infection with Beta or Delta variants.Vaccine. 2023 Nov 22;41(48):7116-7128. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2023.10.018. Epub 2023 Oct 19. Vaccine. 2023. PMID: 37863669 Free PMC article.
-
Therapies for Tau-associated neurodegenerative disorders: targeting molecules, synapses, and cells.Neural Regen Res. 2023 Dec;18(12):2633-2637. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.373670. Neural Regen Res. 2023. PMID: 37449601 Free PMC article.
-
Alzheimer's disease and its treatment-yesterday, today, and tomorrow.Front Pharmacol. 2024 May 24;15:1399121. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1399121. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38868666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
mRNA Vaccine for Alzheimer's Disease: Pilot Study.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Jun 14;12(6):659. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12060659. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38932388 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO. Dementia, key facts, http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs362/en/ (2021).
Grants and funding
- R01 NS-50895/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
- U01 AG060965/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS050895/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG-20241/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Aging (U.S. National Institute on Aging)
- AG20241/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Aging (U.S. National Institute on Aging)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

