Parametrically optimized feather degradation by Bacillus velezensis NCIM 5802 and delineation of keratin hydrolysis by multi-scale analysis for poultry waste management
- PMID: 36224206
- PMCID: PMC9556542
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-21351-9
Parametrically optimized feather degradation by Bacillus velezensis NCIM 5802 and delineation of keratin hydrolysis by multi-scale analysis for poultry waste management
Abstract
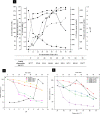
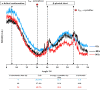
Enormous amounts of keratinaceous waste make a significant and unexploited protein reserve that can be utilized through bioconversion into high-value products using microbial keratinases. This study was intended to assess the keratinase production from a newly isolated B. velezensis NCIM 5802 that can proficiently hydrolyze chicken feathers. Incubation parameters used to produce keratinase enzyme were optimized through the Response Surface Methodology (RSM) with chicken feathers as substrate. Optimization elevated the keratinase production and feather degradation by 4.92-folds (109.7 U/mL) and 2.5 folds (95.8%), respectively. Time-course profile revealed a direct correlation among bacterial growth, feather degradation, keratinase production and amino acid generation. Biochemical properties of the keratinase were evaluated, where it showed optimal activity at 60 °C and pH 10.0. The keratinase was inhibited by EDTA and PMSF, indicating it to be a serine-metalloprotease. Zymography revealed the presence of four distinct keratinases (Mr ~ 100, 62.5, 36.5 and 25 kDa) indicating its multiple forms. NMR and mass spectroscopic studies confirmed the presence of 18 free amino acids in the feather hydrolysates. Changes in feather keratin brought about by the keratinase action were studied by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and spectroscopic (FTIR, Raman) analyses, which showed a decrease in the total crystallinity index (TCI) (1.00-0.63) and confirmed the degradation of its crystalline domain. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) revealed the sequential structural changes occurring in the feather keratin during degradation. Present study explored the use of keratinolytic potential of the newly isolated B. velezensis NCIM 5802 in chicken feather degradation and also, unraveled the underlying keratin hydrolysis mechanism through various analyses.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Wang B, Yang W, McKittrick J, Meyers MA. Keratin: Structure, mechanical properties, occurrence in biological organisms, and efforts at bioinspiration. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016;76:229–318. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2015.06.001. - DOI
-
- Thankaswamy SR, Sundaramoorthy S, Palanivel S, Ramudu KN. Improved microbial degradation of animal hair waste from leather industry using Brevibacterium luteolum (MTCC 5982) J. Clean. Prod. 2018;189:701–708. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.04.095. - DOI
-
- Jagadeesan Y, Meenakshisundaram S, Saravanan V, Balaiah A. Sustainable production, biochemical and molecular characterization of thermo-and-solvent stable alkaline serine keratinase from novel Bacillus pumilus AR57 for promising poultry solid waste management. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020;163:135–146. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.06.219. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

