Impaired amino acid uptake leads to global metabolic imbalance of Candida albicans biofilms
- PMID: 36224215
- PMCID: PMC9556537
- DOI: 10.1038/s41522-022-00341-9
Impaired amino acid uptake leads to global metabolic imbalance of Candida albicans biofilms
Abstract
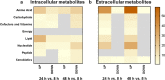
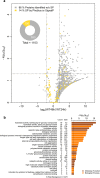
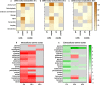
Candida albicans biofilm maturation is accompanied by enhanced expression of amino acid acquisition genes. Three state-of-the-art omics techniques were applied to detail the importance of active amino acid uptake during biofilm development. Comparative analyses of normoxic wild-type biofilms were performed under three metabolically challenging conditions: aging, hypoxia, and disabled amino acid uptake using a strain lacking the regulator of amino acid permeases Stp2. Aging-induced amino acid acquisition and stress responses to withstand the increasingly restricted environment. Hypoxia paralyzed overall energy metabolism with delayed amino acid consumption, but following prolonged adaptation, the metabolic fingerprints aligned with aged normoxic biofilms. The extracellular metabolome of stp2Δ biofilms revealed deficient uptake for 11 amino acids, resulting in extensive transcriptional and metabolic changes including induction of amino acid biosynthesis and carbohydrate and micronutrient uptake. Altogether, this study underscores the critical importance of a balanced amino acid homeostasis for C. albicans biofilm development.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


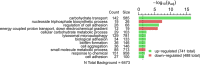

Similar articles
-
The Transcription Factor Stp2 Is Important for Candida albicans Biofilm Establishment and Sustainability.Front Microbiol. 2020 Apr 30;11:794. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00794. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32425915 Free PMC article.
-
GNP2 Encodes a High-Specificity Proline Permease in Candida albicans.mBio. 2022 Feb 22;13(1):e0314221. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03142-21. Epub 2022 Jan 25. mBio. 2022. PMID: 35073760 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of the glycolytic flux and hypoxia adaptation to efficient biofilm formation by Candida albicans.Mol Microbiol. 2011 May;80(4):995-1013. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07626.x. Epub 2011 Apr 6. Mol Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21414038
-
Integration of Posttranscriptional Gene Networks into Metabolic Adaptation and Biofilm Maturation in Candida albicans.PLoS Genet. 2015 Oct 16;11(10):e1005590. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005590. eCollection 2015 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26474309 Free PMC article.
-
The Paralogous Transcription Factors Stp1 and Stp2 of Candida albicans Have Distinct Functions in Nutrient Acquisition and Host Interaction.Infect Immun. 2020 Apr 20;88(5):e00763-19. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00763-19. Print 2020 Apr 20. Infect Immun. 2020. PMID: 32094252 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Metabolic reprogramming during Candida albicans planktonic-biofilm transition is modulated by the transcription factors Zcf15 and Zcf26.PLoS Biol. 2024 Jun 21;22(6):e3002693. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002693. eCollection 2024 Jun. PLoS Biol. 2024. PMID: 38905306 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Understanding the Human Fungal Pathogen Hypoxia Response in Disease Progression.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2023 Sep 15;77:403-425. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-032521-021745. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37713457 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aromatic amino acid metabolism and active transport regulation are implicated in microbial persistence in fractured shale reservoirs.ISME Commun. 2024 Nov 26;4(1):ycae149. doi: 10.1093/ismeco/ycae149. eCollection 2024 Jan. ISME Commun. 2024. PMID: 39670059 Free PMC article.
-
Candida albicans: A Comprehensive View of the Proteome.J Proteome Res. 2025 Apr 4;24(4):1636-1648. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.4c01020. Epub 2025 Mar 14. J Proteome Res. 2025. PMID: 40084908 Free PMC article.
-
An integrated transcriptomic and metabolomic approach to investigate the heterogeneous Candida albicans biofilm phenotype.Biofilm. 2023 Mar 12;5:100112. doi: 10.1016/j.bioflm.2023.100112. eCollection 2023 Dec. Biofilm. 2023. PMID: 36969800 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

