Analysis of hyperforin (St. John's wort) action at TRPC6 channel leads to the development of a new class of antidepressant drugs
- PMID: 36224261
- PMCID: PMC9763113
- DOI: 10.1038/s41380-022-01804-3
Analysis of hyperforin (St. John's wort) action at TRPC6 channel leads to the development of a new class of antidepressant drugs
Abstract
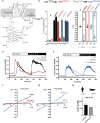
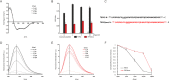
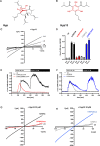
St. John's wort is an herb, long used in folk medicine for the treatment of mild depression. Its antidepressant constituent, hyperforin, has properties such as chemical instability and induction of drug-drug interactions that preclude its use for individual pharmacotherapies. Here we identify the transient receptor potential canonical 6 channel (TRPC6) as a druggable target to control anxious and depressive behavior and as a requirement for hyperforin antidepressant action. We demonstrate that TRPC6 deficiency in mice not only results in anxious and depressive behavior, but also reduces excitability of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons and dentate gyrus granule cells. Using electrophysiology and targeted mutagenesis, we show that hyperforin activates the channel via a specific binding motif at TRPC6. We performed an analysis of hyperforin action to develop a new antidepressant drug that uses the same TRPC6 target mechanism for its antidepressant action. We synthesized the hyperforin analog Hyp13, which shows similar binding to TRPC6 and recapitulates TRPC6-dependent anxiolytic and antidepressant effects in mice. Hyp13 does not activate pregnan-X-receptor (PXR) and thereby loses the potential to induce drug-drug interactions. This may provide a new approach to develop better treatments for depression, since depression remains one of the most treatment-resistant mental disorders, warranting the development of effective drugs based on naturally occurring compounds.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
[Cellular and molecular effects of the antidepressant hyperforin on brain cells: Review of the literature].Encephale. 2014 Apr;40(2):108-13. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2013.03.004. Epub 2013 Jun 29. Encephale. 2014. PMID: 23816060 Review. French.
-
Hyperforin modulates dendritic spine morphology in hippocampal pyramidal neurons by activating Ca(2+) -permeable TRPC6 channels.Hippocampus. 2013 Jan;23(1):40-52. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22052. Epub 2012 Jul 20. Hippocampus. 2013. PMID: 22815087 Free PMC article.
-
No activation of human pregnane X receptor by hyperforin-related phloroglucinols.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2014 Mar;348(3):393-400. doi: 10.1124/jpet.113.209916. Epub 2013 Nov 20. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2014. PMID: 24259679
-
Hyperforin--a key constituent of St. John's wort specifically activates TRPC6 channels.FASEB J. 2007 Dec;21(14):4101-11. doi: 10.1096/fj.07-8110com. Epub 2007 Jul 31. FASEB J. 2007. PMID: 17666455
-
Understanding drug interactions with St John's wort (Hypericum perforatum L.): impact of hyperforin content.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2019 Jan;71(1):129-138. doi: 10.1111/jphp.12858. Epub 2018 Feb 7. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 29411879 Review.
Cited by
-
St. John's wort extract Ze 117 alters the membrane fluidity of C6 glioma cells by influencing cellular cholesterol metabolism.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 30;14(1):9878. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-60562-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38684848 Free PMC article.
-
Hypericin Ameliorates Depression-like Behaviors via Neurotrophin Signaling Pathway Mediating m6A Epitranscriptome Modification.Molecules. 2023 May 3;28(9):3859. doi: 10.3390/molecules28093859. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37175269 Free PMC article.
-
Documentary Analysis of Hypericum perforatum (St. John's Wort) and Its Effect on Depressive Disorders.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Dec 3;17(12):1625. doi: 10.3390/ph17121625. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39770466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Potential of Selected Plants and Their Biologically Active Molecules in the Treatment of Depression and Anxiety Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 6;26(5):2368. doi: 10.3390/ijms26052368. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preventive effect of hyperforin on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury and inflammation by repressing the NF-κB/miR-21 axis.Cent Eur J Immunol. 2024;49(2):169-186. doi: 10.5114/ceji.2024.140636. Epub 2024 Jun 17. Cent Eur J Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39381550 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

