NT157 exerts antineoplastic activity by targeting JNK and AXL signaling in lung cancer cells
- PMID: 36224313
- PMCID: PMC9556623
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-21419-6
NT157 exerts antineoplastic activity by targeting JNK and AXL signaling in lung cancer cells
Abstract
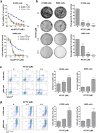
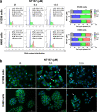
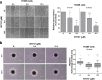
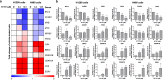
Combination therapies or multi-targeted drugs have been pointed out as an option to prevent the emergence of resistant clones, which could make long-term treatment more effective and translate into better clinical outcomes for cancer patients. The NT157 compound is a synthetic tyrphostin that leads to long-term inhibition of IGF1R/IRS1-2-, STAT3- and AXL-mediated signaling pathways. Given the importance of these signaling pathways for the development and progression of lung cancer, this disease becomes an interesting model for generating preclinical evidence on the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying the antineoplastic activity of NT157. In lung cancer cells, exposure to NT157 decreased, in a dose-dependent manner, cell viability, clonogenicity, cell cycle progression and migration, and induced apoptosis (p < 0.05). In the molecular scenario, NT157 reduced expression of IRS1 and AXL and phosphorylation of p38 MAPK, AKT, and 4EBP1. Besides, NT157 decreased expression of oncogenes BCL2, CCND1, MYB, and MYC and increased genes related to cellular stress and apoptosis, JUN, BBC3, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, FOS, and EGR1 (p < 0.05), favoring a tumor-suppressive cell signaling network in the context of lung cancer. Of note, JNK was identified as a key kinase for NT157-induced IRS1 and IRS2 phosphorylation, revealing a novel axis involved in the mechanism of action of the drug. NT157 also presented potentiating effects on EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer cells. In conclusion, our preclinical findings highlight NT157 as a putative prototype of a multitarget drug that may contribute to the antineoplastic arsenal against lung cancer.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
S.S.K. has research grants from Taiho Pharmaceutical, Johnson & Johnson, MiRXES, and MiNA therapeutics. The other authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
NT157 has antineoplastic effects and inhibits IRS1/2 and STAT3/5 in JAK2V617F-positive myeloproliferative neoplasm cells.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020 Jan 24;5(1):5. doi: 10.1038/s41392-019-0102-5. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020. PMID: 32296029 Free PMC article.
-
NT157, an IGF1R-IRS1/2 inhibitor, exhibits antineoplastic effects in pre-clinical models of chronic myeloid leukemia.Invest New Drugs. 2021 Jun;39(3):736-746. doi: 10.1007/s10637-020-01028-8. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Invest New Drugs. 2021. PMID: 33403501
-
IGF1R/IRS1 targeting has cytotoxic activity and inhibits PI3K/AKT/mTOR and MAPK signaling in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells.Cancer Lett. 2019 Aug 1;456:59-68. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.04.030. Epub 2019 Apr 28. Cancer Lett. 2019. PMID: 31042587
-
Impact of the Anticancer Drug NT157 on Tyrosine Kinase Signaling Networks.Mol Cancer Ther. 2018 May;17(5):931-942. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-17-0377. Epub 2018 Feb 12. Mol Cancer Ther. 2018. PMID: 29440449
-
Targeting Cell Signaling Pathways in Lung Cancer by Bioactive Phytocompounds.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Aug 5;15(15):3980. doi: 10.3390/cancers15153980. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37568796 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Receptor in Tobacco Smoking-Associated Lung Cancer Development.Biomedicines. 2024 Mar 2;12(3):563. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12030563. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38540176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ERα/PR crosstalk is altered in the context of the ERα Y537S mutation and contributes to endocrine therapy-resistant tumor proliferation.NPJ Breast Cancer. 2023 Nov 30;9(1):96. doi: 10.1038/s41523-023-00601-7. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2023. PMID: 38036546 Free PMC article.
-
NT157 exhibits antineoplastic effects by targeting IRS and STAT3/5 signaling in multiple myeloma.Hematol Transfus Cell Ther. 2024 Dec;46 Suppl 6(Suppl 6):S112-S121. doi: 10.1016/j.htct.2024.02.017. Epub 2024 Mar 21. Hematol Transfus Cell Ther. 2024. PMID: 38523043 Free PMC article.
-
Role of early growth response 1 in inflammation-associated lung diseases.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2023 Aug 1;325(2):L143-L154. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00413.2022. Epub 2023 Jul 4. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37401387 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

