Structures of the TMC-1 complex illuminate mechanosensory transduction
- PMID: 36224384
- PMCID: PMC9605866
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-05314-8
Structures of the TMC-1 complex illuminate mechanosensory transduction
Abstract
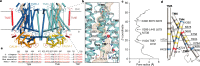
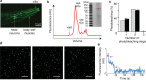
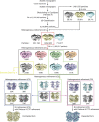
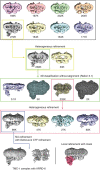
The initial step in the sensory transduction pathway underpinning hearing and balance in mammals involves the conversion of force into the gating of a mechanosensory transduction channel1. Despite the profound socioeconomic impacts of hearing disorders and the fundamental biological significance of understanding mechanosensory transduction, the composition, structure and mechanism of the mechanosensory transduction complex have remained poorly characterized. Here we report the single-particle cryo-electron microscopy structure of the native transmembrane channel-like protein 1 (TMC-1) mechanosensory transduction complex isolated from Caenorhabditis elegans. The two-fold symmetric complex is composed of two copies each of the pore-forming TMC-1 subunit, the calcium-binding protein CALM-1 and the transmembrane inner ear protein TMIE. CALM-1 makes extensive contacts with the cytoplasmic face of the TMC-1 subunits, whereas the single-pass TMIE subunits reside on the periphery of the complex, poised like the handles of an accordion. A subset of complexes additionally includes a single arrestin-like protein, arrestin domain protein (ARRD-6), bound to a CALM-1 subunit. Single-particle reconstructions and molecular dynamics simulations show how the mechanosensory transduction complex deforms the membrane bilayer and suggest crucial roles for lipid-protein interactions in the mechanism by which mechanical force is transduced to ion channel gating.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures









Similar articles
-
The structure of the Caenorhabditis elegans TMC-2 complex suggests roles of lipid-mediated subunit contacts in mechanosensory transduction.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Feb 20;121(8):e2314096121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2314096121. Epub 2024 Feb 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38354260 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of C. elegans TMC-2 complex suggests roles of lipid-mediated subunit contacts in mechanosensory transduction.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Aug 17:2023.08.16.553618. doi: 10.1101/2023.08.16.553618. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Feb 20;121(8):e2314096121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2314096121. PMID: 37645790 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Structure of a eukaryotic cyclic-nucleotide-gated channel.Nature. 2017 Feb 2;542(7639):60-65. doi: 10.1038/nature20819. Epub 2017 Jan 18. Nature. 2017. PMID: 28099415 Free PMC article.
-
Mechano-gated channels in C. elegans.J Neurogenet. 2020 Sep-Dec;34(3-4):363-368. doi: 10.1080/01677063.2020.1832091. Epub 2020 Dec 16. J Neurogenet. 2020. PMID: 33325279 Review.
-
Distinct functions of TMC channels: a comparative overview.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 Nov;76(21):4221-4232. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03214-1. Epub 2019 Oct 4. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31584127 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamics and functions of E-cadherin complexes in epithelial cell and tissue morphogenesis.Mar Life Sci Technol. 2023 Nov 24;5(4):585-601. doi: 10.1007/s42995-023-00206-w. eCollection 2023 Nov. Mar Life Sci Technol. 2023. PMID: 38045551 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanoelectrical transduction-related genetic forms of hearing loss.Curr Opin Physiol. 2023 Apr;32:100632. doi: 10.1016/j.cophys.2023.100632. Epub 2023 Jan 25. Curr Opin Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36936795 Free PMC article.
-
Large-scale growth of C. elegans and isolation of membrane protein complexes.Nat Protoc. 2023 Sep;18(9):2699-2716. doi: 10.1038/s41596-023-00852-5. Epub 2023 Jul 26. Nat Protoc. 2023. PMID: 37495753 Review.
-
Cryo-EM structure of TMEM63C suggests it functions as a monomer.Nat Commun. 2023 Nov 9;14(1):7265. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42956-2. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37945568 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Druggable Binding Sites and Small Molecules as Modulators of TMC1.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 20:2024.03.05.583611. doi: 10.1101/2024.03.05.583611. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Commun Biol. 2025 May 13;8(1):742. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-07943-x. PMID: 38826329 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Musiek, F. E. & Baran, J. A. The Auditory System: Anatomy, Physiology, and Clinical Correlates, 2nd edn (Plural Publishing, 2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

