Neoadjuvant toripalimab combined with gemcitabine and cisplatin in resectable locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (NeoTGP01): An open label, single-arm, phase Ib clinical trial
- PMID: 36224603
- PMCID: PMC9558942
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-022-02510-2
Neoadjuvant toripalimab combined with gemcitabine and cisplatin in resectable locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (NeoTGP01): An open label, single-arm, phase Ib clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Neoadjuvant programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1) inhibitors have drawn increasing attention in locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). In this study, we investigated the safety and efficacy of gemcitabine and cisplatin (GP), combined with a PD-1 inhibitor, in patients with locally advanced HNSCC.
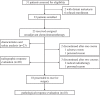
Materials and methods: A total of 23 eligible patients were administered two cycles of toripalimab and GP followed by surgical resection. The primary endpoints were safety, treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs), and non-operation delay rates. The secondary endpoints consisted of pathological complete response (pCR) rate, major pathological response (MPR) rate, objective response rate (ORR), and R0 resection rate.
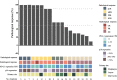
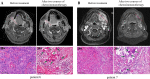
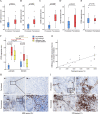
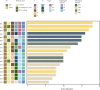
Results: The incidence of TRAEs from grades 1 to 4 was 43.5%, 34.8%, 13.0%, and 8.7%, respectively. Grade 3/4 TRAEs included neutropenia, fatigue, hyperglycemia, nausea and vomiting, decreased appetite, rash, and diarrhea. No treatment-related surgical delay was observed. The radiographic response rates were 5.0% (CR), 40.0% (PR), and 55.0% (SD). The ORR reached 45.0%. Eighteen patients underwent successful surgical resection. The R0 resection rate was 100%. The pathological response rates were 16.7% (pCR), 27.8% (MPR, two of five near-pCR), 16.7% (PPR), and 38.8% (NPR). CD4, CD8, CD20, and CD38 expression in the tumors significantly increased after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. The increase in CD20 levels after neoadjuvant treatment in patients with pCR/MPR was significantly higher than in patients with PPR/NPR.
Conclusion: Triweekly neoadjuvant toripalimab-GP is feasible and achieves promising pCR and MPR rates in patients with resectable locally advanced HNSCC.
Trial registration: Chinese clinical trial registry, ChiCTR2100043743, Registered 27 Febrary 2021- Retrospectively registered, http://www.chictr.org.cn/showproj.aspx?proj=120570.
Keywords: Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; Immunotherapy; Neoadjuvant treatment; Pathological response rate.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Burtness B, Harrington KJ, Greil R, Soulières D, Tahara M, De Castro G, et al. KEYNOTE-048: Phase III study of first-line pembrolizumab (P) for recurrent/metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (R/M HNSCC). Annals of Oncology. 2018;29.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

