Current understanding of epigenetics role in melanoma treatment and resistance
- PMID: 36224606
- PMCID: PMC9555085
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-022-02738-0
Current understanding of epigenetics role in melanoma treatment and resistance
Abstract
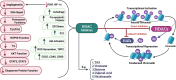
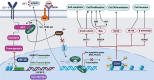
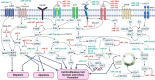
Melanoma is the most aggressive form of skin cancer resulting from genetic mutations in melanocytes. Several factors have been considered to be involved in melanoma progression, including genetic alteration, processes of damaged DNA repair, and changes in mechanisms of cell growth and proliferation. Epigenetics is the other factor with a crucial role in melanoma development. Epigenetic changes have become novel targets for treating patients suffering from melanoma. These changes can alter the expression of microRNAs and their interaction with target genes, which involves cell growth, differentiation, or even death. Given these circumstances, we conducted the present review to discuss the melanoma risk factors and represent the current knowledge about the factors related to its etiopathogenesis. Moreover, various epigenetic pathways, which are involved in melanoma progression, treatment, and chemo-resistance, as well as employed epigenetic factors as a solution to the problems, will be discussed in detail.
Keywords: Drug resistance; Epigenetics; Immunotherapy; Melanoma.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
There are no competing interests declared by the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epigenetics in human melanoma.Cancer Control. 2009 Jul;16(3):200-18. doi: 10.1177/107327480901600302. Cancer Control. 2009. PMID: 19556960 Review.
-
Epigenetics of melanoma: implications for immune-based therapies.Immunotherapy. 2013 Oct;5(10):1103-16. doi: 10.2217/imt.13.108. Immunotherapy. 2013. PMID: 24088079 Review.
-
Melanoma epigenetics: novel mechanisms, markers, and medicines.Lab Invest. 2014 Aug;94(8):822-38. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2014.87. Epub 2014 Jun 30. Lab Invest. 2014. PMID: 24978641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetics and cutaneous neoplasms: from mechanism to therapy.Epigenomics. 2023 Feb;15(3):167-187. doi: 10.2217/epi-2023-0016. Epub 2023 Apr 5. Epigenomics. 2023. PMID: 37020393 Review.
-
The "ART" of Epigenetics in Melanoma: From histone "Alterations, to Resistance and Therapies".Theranostics. 2020 Jan 1;10(4):1777-1797. doi: 10.7150/thno.36218. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32042336 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Review of Advanced Cutaneous Melanoma Therapies and Their Mechanisms, from Immunotherapies to Lysine Histone Methyl Transferase Inhibitors.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Dec 8;15(24):5751. doi: 10.3390/cancers15245751. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136297 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling the Dynamic Interplay between Cancer Stem Cells and the Tumor Microenvironment in Melanoma: Implications for Novel Therapeutic Strategies.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Aug 16;16(16):2861. doi: 10.3390/cancers16162861. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199632 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA hypermethylation of tumor suppressor genes among oral squamous cell carcinoma patients: a prominent diagnostic biomarker.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Dec 7;52(1):44. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-10144-0. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39644423 Review.
-
Integrated analysis reveals SMARCD1 is a potential biomarker and therapeutic target in skin cutaneous melanoma.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Oct;149(13):11619-11634. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05064-8. Epub 2023 Jul 4. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37401939 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk in Skin: Loss of Desmoglein 1 in Keratinocytes Inhibits BRAFV600E-Induced Cellular Senescence in Human Melanocytes.J Invest Dermatol. 2025 Jul;145(7):1740-1752.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2024.10.608. Epub 2024 Nov 23. J Invest Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 39581457
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

