High-coverage targeted lipidomics could reveal lipid alterations and evaluate therapeutic efficacy of membranous nephropathy
- PMID: 36224633
- PMCID: PMC9559911
- DOI: 10.1186/s12986-022-00701-4
High-coverage targeted lipidomics could reveal lipid alterations and evaluate therapeutic efficacy of membranous nephropathy
Abstract
Background: Membrane nephropathy (MN) often presents as nephrotic syndrome with characteristic lipid metabolism that could not be explained by lipid indicators commonly used in clinical practice. Studies have shown that invigorating spleen and qi, activating blood and detoxication in the treatment of MN is an effective method proved by randomized controlled clinical trial. However, the alterations of lipid profile before and after traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) treatment and the related lipid markers that affect the therapeutic effect have not been fully clarified.
Methods: We analyzed plasma lipid profiles of 92 patients with MN before and after TCM treatment by high-coverage targeted lipidomics.
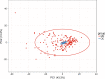
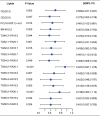
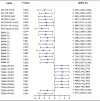
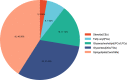
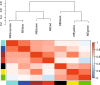
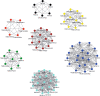
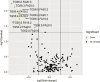
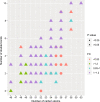
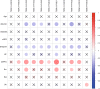
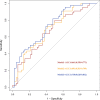
Results: 675 lipids were identified, of which 368 stably expressed lipids (coefficient of variation less than 30% and deletion value less than 10%) were eventually included for statistical analysis. 105 lipids were altered mainly including spingolipids, glycerides, glycerophosholipid, fatty acyl and steroids, among which, the abundance of ceramides (Cers), sphingomyelins (SMs), diacylglycerols (DGs), phosphatidylcholines (PCs) were lower than those before treatment with statistically significant difference. The WGCNA network to analyze the correlation between the collective effect and the therapeutic effect showed that the triglyceride (TG) molecules were most relevant to the therapeutic effect. Analysis of 162 triglyceride molecules showed that 11 TGs were significantly down-regulated in the effective group which were concentrated in carbon atom number of 52-56 and double bond number of 0-4. TGs molecules including TG56:2-FA20:0, TG56:2-FA20:1, TG56:3-FA20:0 and TG56:5-FA20:2 were most closely related to the therapeutic effect of TCM after adjusting the influence of clinical factors. ROC curve analysis showed that these four lipids could further improve the predictive efficacy of treatment based on clinical indicators.
Conclusion: Our work demonstrated that the therapeutic effect of invigorating spleen and qi, activating blood and detoxication in the treatment of MN may be exerted by regulating lipid metabolism. High-coverage targeted lipidomics provided a non-invasive tool for discovery of lipid markers to improve the predictive efficacy of TCM therapy.
Keywords: High-coverage targeted; Lipidomics; Membranous nephropathy; Traditional Chinese medicine.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Combining lipidomics and efficacy-oriented compatibility revealed that Qi Ge decoction compatibility improved lipid metabolism in hyperlipidemic rats.Biomed Chromatogr. 2023 May;37(5):e5595. doi: 10.1002/bmc.5595. Epub 2023 Feb 16. Biomed Chromatogr. 2023. PMID: 36734105
-
Lipidomics reveals association of circulating lipids with body mass index and outcomes in IgA nephropathy patients.J Mol Cell Biol. 2021 Jul 17;13(8):565-75. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjab040. Online ahead of print. J Mol Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 34272854 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy and safety of Chinese herbal medicine Shen-Qi Hua-Yu formula in patients with diabetic lower extremity artery disease: Study protocol of a multi-center, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Jan;99(3):e18713. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000018713. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32011447 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional Chinese Medicine as an adjunct therapy in the treatment of idiopathic membranous nephropathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2021 May 14;16(5):e0251131. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0251131. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33989325 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of clinical evidence on traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy: a comprehensive review with evidence mapping.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Mar 27;15:1324782. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1324782. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38601203 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chewing the fat: How lipidomics is changing our understanding of human health and disease in 2022.Anal Sci Adv. 2023 May 10;4(3-4):104-131. doi: 10.1002/ansa.202300009. eCollection 2023 May. Anal Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 38715925 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

