Dietary supplementation of Macleaya cordata extract and Bacillus in combination improve laying performance by regulating reproductive hormones, intestinal microbiota and barrier function of laying hens
- PMID: 36224643
- PMCID: PMC9559840
- DOI: 10.1186/s40104-022-00766-4
Dietary supplementation of Macleaya cordata extract and Bacillus in combination improve laying performance by regulating reproductive hormones, intestinal microbiota and barrier function of laying hens
Abstract
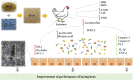
Background: This study aimed to investigate whether the combination of Macleaya cordata extract (MCE) and Bacillus could improve the laying performance and health of laying hens better.
Methods: A total of 360 29-week-old Jingbai laying hens were randomly divided into 4 treatments: control group (basal diet), MCE group (basal diet + MCE), Probiotics Bacillus Compound (PBC) group (basal diet + compound Bacillus), MCE + PBC group (basal diet + MCE + compound Bacillus). The feeding experiment lasted for 42 d.
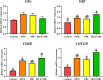
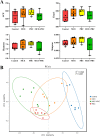
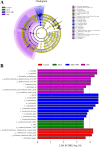
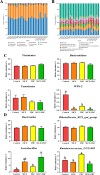
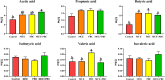
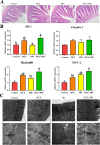
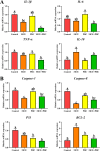
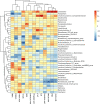
Results: The results showed that the laying rate and the average daily egg mass in the MCE + PBC group were significantly higher than those in the control group (P < 0.05) and better than the MCE and PBC group. Combination of MCE and Bacillus significantly increased the content of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) in the serum and up-regulated the expression of related hormone receptor gene (estrogen receptor-β, FSHR and luteinizing hormone/choriogonadotropin receptor) in the ovary of laying hens (P < 0.05). In the MCE + PBC group, the mRNA expressions of zonula occluden-1, Occludin and mucin-2 in jejunum was increased and the intestinal epithelial barrier detected by transmission electron microscopy was enhanced compared with the control group (P < 0.05). In addition, compared with the control group, combination of MCE and Bacillus significantly increased the total antioxidant capacity and catalase activity (P < 0.05), and down-regulated the mRNA expressions of inflammation-related genes (interleukin-1β and tumor necrosis factor-α) as well as apoptosis-related genes (Caspase 3, Caspase 8 and P53) (P < 0.05). The concentration of acetic acid and butyric acid in the cecum content of laying hens in the MCE + PBC group was significantly increased compared with the control group (P < 0.05).
Conclusions: Collectively, dietary supplementation of 600 μg/kg MCE and 5 × 108 CFU/kg compound Bacillus can improve laying performance by improving microbiota to enhance antioxidant capacity and intestinal barrier, regulate reproductive hormones and the concentration of cecal short-chain fatty acids of laying hens, and the combined effect of MCE and Bacillus is better than that of single supplementation.
Keywords: Bacillus; Intestinal microbiota; Laying hens; Laying performance; Macleaya cordata extract; Reproductive hormones.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

