The Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway in Haematological Neoplasms
- PMID: 36224652
- PMCID: PMC9558365
- DOI: 10.1186/s40364-022-00418-9
The Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway in Haematological Neoplasms
Abstract
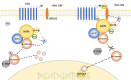
Leukaemia and lymphoma are common malignancies. The Wnt pathway is a complex network of proteins regulating cell proliferation and differentiation, as well as cancer development, and is divided into the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway (the canonical Wnt signalling pathway) and the noncanonical Wnt signalling pathway. The Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway is highly conserved evolutionarily, and activation or inhibition of either of the pathways may lead to cancer development and progression. The aim of this review is to analyse the mechanisms of action of related molecules in the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in haematologic malignancies and their feasibility as therapeutic targets.
Keywords: Haematologic neoplasms; Leukaemia; Lymphoma; Multiple myeloma; Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Crosstalk between long non-coding RNAs and Wnt/β-catenin signalling in cancer.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Apr;22(4):2062-2070. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13522. Epub 2018 Feb 1. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29392884 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wnt-β-catenin signalling in liver development, health and disease.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Feb;16(2):121-136. doi: 10.1038/s41575-018-0075-9. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30451972 Review.
-
Wnt signalling pathways in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia and B-cell lymphomas.Br J Pharmacol. 2017 Dec;174(24):4701-4715. doi: 10.1111/bph.13949. Epub 2017 Aug 30. Br J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28703283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calreticulin mediated glucocorticoid receptor export is involved in beta-catenin translocation and Wnt signalling inhibition in human osteoblastic cells.Bone. 2009 Apr;44(4):555-65. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2008.11.013. Epub 2008 Dec 3. Bone. 2009. PMID: 19100874
-
Constitutive activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin signalling pathway in acute myeloid leukaemia.Oncogene. 2005 Mar 31;24(14):2410-20. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208431. Oncogene. 2005. PMID: 15735743
Cited by
-
Canonical WNT/β-catenin signaling upregulates aerobic glycolysis in diverse cancer types.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Jul 6;51(1):788. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09694-0. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38970704 Review.
-
Dujieqing decoction suppresses multiple myeloma growth by inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.J Tradit Chin Med. 2025 Aug;45(4):720-729. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.04.002. J Tradit Chin Med. 2025. PMID: 40810217 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt signaling - using the bloodstream to send a message.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025 Aug 29;82(1):322. doi: 10.1007/s00018-025-05863-x. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40879783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KIF18B: an important role in signaling pathways and a potential resistant target in tumor development.Discov Oncol. 2024 Sep 11;15(1):430. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01330-4. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39259333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nkd1 functions downstream of Axin2 to attenuate Wnt signaling.Mol Biol Cell. 2024 Jul 1;35(7):ar93. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E24-02-0059-T. Epub 2024 Apr 24. Mol Biol Cell. 2024. PMID: 38656801 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vleminckx K, Wong E, Guger K, Rubinfeld B, Polakis P, Gumbiner BM. Adenomatous polyposis coli tumor suppressor protein has signaling activity in Xenopus laevis embryos resulting in the induction of an ectopic dorsoanterior axis. J Cell Biol. 1997;136(2):411–20. doi: 10.1083/jcb.136.2.411. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
- No. 81372134/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- No. 81372134/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- No. 2021JJ30590/Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province
- No. 2021JJ30590/Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province
- 2014-405/Hunan Province Cooperative Innovation Center for Molecular Target New Drug Study
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

