Exploring the Active Ingredients and Mechanism of Action of Huanglian Huazhuo Capsule for the Treatment of Obese Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus Based on Using Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking
- PMID: 36225181
- PMCID: PMC9550451
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/2780647
Exploring the Active Ingredients and Mechanism of Action of Huanglian Huazhuo Capsule for the Treatment of Obese Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus Based on Using Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking
Abstract
Background: Obese type 2 diabetes mellitus (obese T2DM) is one of the prime diseases that endangers human health. Clinical studies have confirmed the ability of the Huanglian Huazhuo capsule to treat obese T2DM; however, its mechanism of action is still unclear. In this study, effects and mechanisms of the Huanglian Huazhuo capsule in obese T2DM were systematically investigated using network pharmacology and molecular docking techniques.
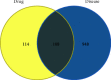
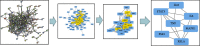
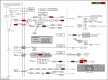
Methods: The active ingredients and targets of the Huanglian Huazhuo capsule were extracted from Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database and Analysis Platform (TCMSP). Obese T2DM diabetes-related targets were retrieved from a geographic dataset combined with a gene card database. A protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was constructed to screen core targets. The Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analyses were conducted using Database for Annotation Visualization and Integrated Discovery (DAVID). Interactions between potential targets and active compounds were assessed using molecular docking. Molecular docking was performed on the best core protein complexes obtained using molecular docking.
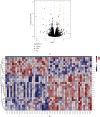
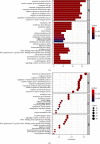
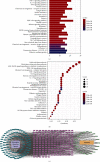
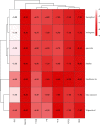
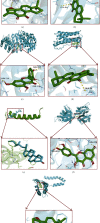
Results: A total of 89 and 108 active ingredients and targets, respectively, were identified. Seven core targets were obtained using a topological analysis of the PPI network. The GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analyses showed that the effects of the Huanglian Huazhuo capsules were mediated by inflammation, lipid response, oxidative stress-related genes, and HIF-1 and IL-17 signaling pathways. Good binding ability was observed between the active compounds and screened targets using molecular docking.
Conclusions: The active ingredients, potential targets, and pathways of the Huanglian Huazhuo capsule for the treatment of obese T2DM were successfully predicted, providing a new strategy for further investigation of its molecular mechanisms. In addition, the potential active ingredients provide a reliable source for drug screening in obese T2DM.
Copyright © 2022 Na Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this work have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Systems Pharmacology-based Drug Discovery and Active Mechanism of Ganoderma lucidum Triterpenoids for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus by Integrating Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking.Curr Pharm Des. 2025 Feb 13. doi: 10.2174/0113816128365423250126035306. Online ahead of print. Curr Pharm Des. 2025. PMID: 39949090
-
Exploring the mechanism of Jingshen Xiaoke decoction in treating T2DM mice based on network pharmacology and molecular docking.Technol Health Care. 2024;32(1):163-179. doi: 10.3233/THC-220630. Technol Health Care. 2024. PMID: 37092194
-
Mechanisms underlying the therapeutic effects of Qingfeiyin in treating acute lung injury based on GEO datasets, network pharmacology and molecular docking.Comput Biol Med. 2022 Jun;145:105454. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105454. Epub 2022 Mar 26. Comput Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 35367781
-
Network pharmacology prediction and molecular docking-based strategy to explore the potential mechanism of Huanglian Jiedu Decoction against sepsis.Comput Biol Med. 2022 May;144:105389. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105389. Epub 2022 Mar 9. Comput Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 35303581 Review.
-
Use of bailing capsules (cordyceps sinensis) in the treatment of chronic kidney disease: a meta-analysis and network pharmacology.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Apr 5;15:1342831. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1342831. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38645562 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bioactive Compounds in Citrus reticulata Peel Are Potential Candidates for Alleviating Physical Fatigue through a Triad Approach of Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamics Modeling.Nutrients. 2024 Jun 18;16(12):1934. doi: 10.3390/nu16121934. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38931288 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of 6-Shogaol on Glucose Uptake and Intestinal Barrier Integrity in Caco-2 Cells.Foods. 2023 Jan 21;12(3):503. doi: 10.3390/foods12030503. Foods. 2023. PMID: 36766032 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhou Z. Internal Medicine in Chinese Medicine . 2. Beijing, China: China Chinese Medicine Press; 2007. p. p. 407.
-
- Saimaiti M., yisrieeli M., Aili A. Research progress on the relationship between obesity and type 2 diabetes. Chinese Electronic Journal of obesity and metabolic diseases . 2020;6(2):130–134.
-
- Zheng K., Geng J., Liu Q. Effect of insulin treatment of primary obese T2DM patients combined with liraglutide on microinflammation and B-cell function. Chinese Journal of Gerontology . 2019;39(20):4917–4920.
-
- Zhong Q. Clinical Study on the Treatment of Obesity-type Diabetes Mellitus with Liver and Stomach Stagnation and Heat with Stasis . Jiangsu, China: Nanjing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; 2012.
-
- An S., Cui Q. R., Kang X. D., Wang D. K. Clinical study on the combination of Huanglian Huahuo formula and metformin in the treatment of obese type 2 diabetes mellitus combined with dyslipidemia. Western Chinese Medicine . 2021;34(09):99–102.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

