Metagenomic analysis of the soil microbial composition and salt tolerance mechanism in Yuncheng Salt Lake, Shanxi Province
- PMID: 36225369
- PMCID: PMC9549588
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1004556
Metagenomic analysis of the soil microbial composition and salt tolerance mechanism in Yuncheng Salt Lake, Shanxi Province
Abstract
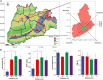
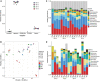
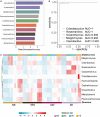
The soil in Yuncheng Salt Lake has serious salinization and the biogeographic environment affects the composition and distribution of special halophilic and salt-tolerant microbial communities in this area. Therefore, this study collected soils at distances of 15, 30, and 45 m from the Salt Lake and used non-saline soil (60 m) as a control to explore the microbial composition and salt tolerance mechanisms using metagenomics technology. The results showed that the dominant species and abundance of salt-tolerant microorganisms changed gradually with distance from Salt Lake. The salt-tolerant microorganisms can increase the expression of the Na+/H+ antiporter by upregulating the Na+/H+ antiporter subunit mnhA-G to respond to salt stress, simultaneously upregulating the genes in the betaine/proline transport system to promote the conversion of choline into betaine, while also upregulating the trehalose/maltose transport system encode genes to promote the synthesis of trehalose to resist a high salt environment.
Keywords: Salt Lake; metagenome; microbial composition; salt tolerance mechanism; soil microorganism.
Copyright © 2022 Zeng, Zhu, Zhang, Zhao, Li, Ma, Zhang, Wang, Wu, Guo and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Metagenomic Insights into Microbial Community Structure, Function, and Salt Adaptation in Saline Soils of Arid Land, China.Microorganisms. 2022 Nov 3;10(11):2183. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10112183. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36363774 Free PMC article.
-
Patterns in the Microbial Community of Salt-Tolerant Plants and the Functional Genes Associated with Salt Stress Alleviation.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Oct 31;9(2):e0076721. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00767-21. Epub 2021 Oct 27. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34704793 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial community in saline farmland soil on the Tibetan plateau: responding to salinization while resisting extreme environments.BMC Microbiol. 2021 Apr 20;21(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s12866-021-02190-6. BMC Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33874905 Free PMC article.
-
Microbially Mediated Plant Salt Tolerance and Microbiome-based Solutions for Saline Agriculture.Biotechnol Adv. 2016 Nov 15;34(7):1245-1259. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2016.08.005. Epub 2016 Aug 30. Biotechnol Adv. 2016. PMID: 27587331 Review.
-
Traversing the "Omic" landscape of microbial halotolerance for key molecular processes and new insights.Crit Rev Microbiol. 2020 Nov;46(6):631-653. doi: 10.1080/1040841X.2020.1819770. Epub 2020 Sep 29. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32991226 Review.
Cited by
-
Microbial Assembly and Stress-Tolerance Mechanisms in Salt-Adapted Plants Along the Shore of a Salt Lake: Implications for Saline-Alkaline Soil Remediation.Microorganisms. 2025 Aug 20;13(8):1942. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13081942. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40871446 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization, diversity, and biogeochemical potential of soil viruses inhabiting in Yuncheng Salt Lake.Front Microbiol. 2025 May 7;16:1597514. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1597514. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40400689 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring biogeochemical transformation in a hypertrophic lake with dual focus on environmental cues and potential functional fingerprints of littoral bacteria.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 24;15(1):31115. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-16527-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40851025 Free PMC article.
-
Bioprospecting of Actinobacterial Diversity and Antibacterial Secondary Metabolites from the Sediments of Four Saline Lakes on the Northern Tibetan Plateau.Microorganisms. 2023 Oct 1;11(10):2475. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11102475. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37894133 Free PMC article.
-
Limited Microbial Contribution in Salt Lake Sediment and Water to Each Other's Microbial Communities.Microorganisms. 2024 Dec 9;12(12):2534. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12122534. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39770736 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anburajan L., Meena B., Vinithkumar N. V., Kirubagaran R., Dharani G. (2019). Functional characterization of a major compatible solute in deep sea halophilic eubacteria of active volcanic Barren Island, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India. Infect. Genet. Evol. 73 261–265. 10.1016/j.meegid.2019.05.008 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Banciu H. L., Enache M., Rodriguez R. M., Oren A., Ventosa A. (2019). Ecology and physiology of halophilic microorganisms - Thematic issue based on papers presented at Halophiles 2019 - 12th international conference on halophilic microorganisms, Cluj-Napoca, Romania, 24-28 June, 2019. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 366:fnz250. 10.1093/femsle/fnz250 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cazzulo J. J., Vidal M. C., Massarini E. (1973). Proceedings: Regulatory properties of enzymes from halophilic bacteria. Acta Physiol. Lat. Am. 23 578–580. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

