Apolipoprotein-A-I for severe COVID-19-induced hyperinflammatory states: A prospective case study
- PMID: 36225555
- PMCID: PMC9550000
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.936659
Apolipoprotein-A-I for severe COVID-19-induced hyperinflammatory states: A prospective case study
Abstract
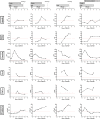
Viral infections can promote cytokine storm and multiorgan failure in individuals with an underlying immunosuppression or specific genetic background. Hyperinflammatory states, including critical forms of COVID-19, are characterized by a remodeling of the lipid profile including a dramatic decrease of the serum levels of apolipoprotein-A-I (ApoA-I), a protein known for its capacity to reduce systemic and lung inflammation, modulate innate and adaptive immunity, and prevent endothelial dysfunction and blood coagulation. In this study, four immunocompromised patients with severe COVID-19 cytokine storm that progressed despite standard-of-care therapy [Omicron (n = 3) and Delta (n = 1) variants] received 2- 4 infusions (10 mg/kg) of CER-001, an ApoA-I-containing HDL mimetic. Injections were well-tolerated with no serious adverse events. Three patients treated while not on mechanical ventilation had early clinical and biological improvement (oxygen withdrawal and correction of hematological and inflammatory parameters, including serum levels of interleukin-8) and were discharged from the hospital 3-4 days after CER-001 infusions. In the fourth patient who received CER-001 after orotracheal intubation for acute respiratory distress syndrome, infusions were followed by transient respiratory improvement before secondary worsening related to ventilation-associated pneumonia. This pilot uncontrolled exploratory compassionate study provides initial safety and proof-of-concept data from patients with a COVID-19 cytokine storm receiving ApoA-I. Further randomized controlled trial evaluation is now required to ascertain whether ApoA-I has any beneficial effects on patients with a COVID-19 cytokine storm.
Keywords: ApoA-I; COVID-19; HDL; apolipoprotein-A-I; cytokine storm; endothelium; inflammation.
Copyright © 2022 Faguer, Del Bello, Danet, Renaudineau, Izopet and Kamar.
Conflict of interest statement
SF has received personal consulting fees from Abionyx Pharma for the development of CER-001 in LCAT deficiency related-glomerulopathy. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Cho K. H., Kim J. R., Lee I. C., Kwon H. J. (2021). Native high-density lipoproteins (HDL) with higher paraoxonase exerts a potent antiviral effect against SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19), while glycated HDL lost the antiviral activity. Antioxidants (Basel) 10, 209–211. 10.3390/antiox10020209 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources