Methotrexate showed efficacy both in Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, predictors of surgery were identified in patients initially treated with methotrexate monotherapy
- PMID: 36225564
- PMCID: PMC9548616
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.996065
Methotrexate showed efficacy both in Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, predictors of surgery were identified in patients initially treated with methotrexate monotherapy
Abstract
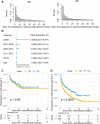
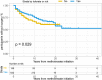
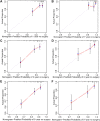
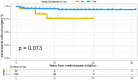
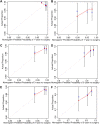
Objective: This study aimed to evaluate methotrexate efficacy in patients with Crohn's disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC), and identify predictors of surgery for patients who were initially treated with methotrexate monotherapy. Design: We performed a retrospective analysis of 34,860 patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in the IBD Bioresource (United Kingdom) prior to 9 November 2021. Logistic regression was used to identify factors associated with methotrexate efficacy. The data were randomly stratified into training and testing sets (7:3). Nomograms were developed based on Cox regression analysis outcomes. The predictive accuracy and discriminative ability were determined using the concordance index (C-index) and calibration curves. Results: Overall, 1,042 patients (CD: 791, UC: 251) were included. Independent factors associated with effective methotrexate monotherapy were younger age at diagnosis, latest therapy period, exclusive upper gastrointestinal tract disease (for CD), and longer duration between diagnosis and methotrexate initiation (for UC). For CD, predictors in the nomogram were gender, treatment era, tolerance, lesion site, perianal involvement, disease behaviour, and biologics requirements (C-index: 0.711 and 0.732 for training and validation cohorts, respectively). For UC, the factors were age at diagnosis and sex (C-index: 0.784 and 0.690 for training and validation cohorts, respectively). Calibration curves demonstrated good agreement between predictions and actual observations.
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; inflammatory bowel disease; methotrexate monotherapy; prognostic analysis; ulcerative colitis.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Zhao, Wang, Zheng, Chang and Sang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Carbonnel F., Colombel J. F., Filippi J., Katsanos K. H., Peyrin-Biroulet L., Allez M., et al. (2016). Methotrexate is not superior to placebo for inducing steroid-free remission, but induces steroid-free clinical remission in a larger proportion of patients with ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology 150 (2), 380–388. e4. 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.10.050 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cervoni J. P., Alby-Lepresle B., Weil D., Zhong P., Aubin F., Wendling D., et al. (2020). A pragmatic non-invasive assessment of liver fibrosis in patients with psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis or Crohn's disease receiving methotrexate therapy. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 44S, 100003. 10.1016/j.clirex.2020.100003 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

