Selective miRNA inhibition in CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes enhances HIV-1 specific cytotoxic responses
- PMID: 36225912
- PMCID: PMC9549323
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.998368
Selective miRNA inhibition in CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes enhances HIV-1 specific cytotoxic responses
Abstract
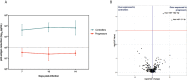
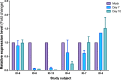
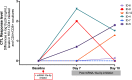
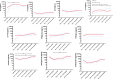
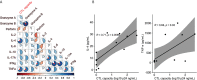
miRNAs dictate relevant virus-host interactions, offering new avenues for interventions to achieve an HIV remission. We aimed to enhance HIV-specific cytotoxic responses-a hallmark of natural HIV control- by miRNA modulation in T cells. We recruited 12 participants six elite controllers and six patients with chronic HIV infection on long-term antiretroviral therapy ("progressors"). Elite controllers exhibited stronger HIV-specific cytotoxic responses than the progressors, and their CD8+T cells showed a miRNA (hsa-miR-10a-5p) significantly downregulated. When we transfected ex vivo CD8+ T cells from progressors with a synthetic miR-10a-5p inhibitor, miR-10a-5p levels decreased in 4 out of 6 progressors, correlating with an increase in HIV-specific cytotoxic responses. The effects of miR-10a-5p inhibition on HIV-specific CTL responses were modest, short-lived, and occurred before day seven after modulation. IL-4 and TNF-α levels strongly correlated with HIV-specific cytotoxic capacity. Thus, inhibition of miR-10a-5p enhanced HIV-specific CD8+ T cell capacity in progressors. Our pilot study proves the concept that miRNA modulation is a feasible strategy to combat HIV persistence by enhancing specific cytotoxic immune responses, which will inform new approaches for achieving an antiretroviral therapy-free HIV remission.
Keywords: HIV; cellular immunity; cytotoxicity; micro-RNA; non-coding RNA.
Copyright © 2022 Madrid-Elena, Serrano-Villar, Gutiérrez, Sastre, Morín, Luna, Martín, Santoyo-López, López-Huertas, Moreno, García-Bermejo, Moreno-Pelayo and Moreno.
Conflict of interest statement
Outside the submitted work, author SS-V reports personal fees from ViiV Healthcare, Janssen Cilag, Gilead Sciences, and MSD as well as non-financial support from ViiV Healthcare and Gilead Sciences and research grants from MSD and Gilead Sciences. Author SM reports grants, personal fees and non-financial support from ViiV Healthcare, personal fees and non-financial support from Janssen, grants, personal fees and non-financial support from MSD, grants, personal fees and non-financial support from Gilead. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Alterations in Abundance and Compartmentalization of miRNAs in Blood Plasma Extracellular Vesicles and Extracellular Condensates during HIV/SIV Infection and Its Modulation by Antiretroviral Therapy (ART) and Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC).Viruses. 2023 Feb 24;15(3):623. doi: 10.3390/v15030623. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36992332 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon Alpha Enhances NK Cell Function and the Suppressive Capacity of HIV-Specific CD8+ T Cells.J Virol. 2019 Jan 17;93(3):e01541-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01541-18. Print 2019 Feb 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30404799 Free PMC article.
-
Cytotoxic CD8+ T Cells Expressing CXCR5 Are Detectable in HIV-1 Elite Controllers After Prolonged In Vitro Peptide Stimulation.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 24;11:622343. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.622343. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33717056 Free PMC article.
-
Immunologic Control of HIV-1: What Have We Learned and Can We Induce It?Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2021 Jun;18(3):211-220. doi: 10.1007/s11904-021-00545-2. Epub 2021 Mar 11. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2021. PMID: 33709324 Review.
-
Immune Responses in Controllers of HIV Infection.Annu Rev Immunol. 2024 Jun;42(1):21-33. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-083122-035233. Epub 2024 Jun 14. Annu Rev Immunol. 2024. PMID: 37827174 Review.
Cited by
-
A new perspective on HIV: effects of HIV on brain-heart axis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Aug 4;10:1226782. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1226782. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37600062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs in Cancer Immunology: Master Regulators of the Tumor Microenvironment and Immune Evasion, with Therapeutic Potential.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jun 27;17(13):2172. doi: 10.3390/cancers17132172. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40647470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs: Small but Key Players in Viral Infections and Immune Responses to Viral Pathogens.Biology (Basel). 2023 Oct 14;12(10):1334. doi: 10.3390/biology12101334. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37887044 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

