A vicious circle in breast cancer: The interplay between inflammation, reactive oxygen species, and microRNAs
- PMID: 36226048
- PMCID: PMC9548555
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.980694
A vicious circle in breast cancer: The interplay between inflammation, reactive oxygen species, and microRNAs
Abstract
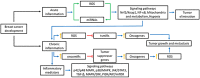
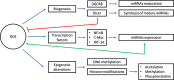
Breast cancer (BC) is the most common cancer in women worldwide. This highly heterogeneous disease is molecularly stratified into luminal A, luminal B, HER2, triple-negative/basal-like, and normal-like subtypes. An important aspect in BC progression is the activation of inflammatory processes. The activation of CD8+/Th1, NK, and M1 tumor associated macrophages (TAMs), leads to tumor destruction. In contrast, an anti-inflammatory response mediated by CD4+/Th2 and M2 TAMs will favor tumor progression. Inflammation also stimulates the production of inflammatory mediators like reactive oxygen species (ROS). In chronic inflammation, ROS activates oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction. In cancer, ROS plays a dual role with anti-tumorigenic and pro-tumorigenic effects in cell signaling pathways that control proliferation, survival, apoptosis, and inflammation. MicroRNAs (miRNAs), which are known to be involved in BC progression and inflammation, can be regulated by ROS. At the same time, miRNAs regulate the expression of genes modulating oxidative stress. In this review, we will discuss the interplay between inflammation, ROS, and miRNAs as anticancer and tumor promoter molecules in BC. A clear understanding of the role of miRNAs in the regulation of ROS production and inflammation, may lead to new opportunities for therapy in BC.
Keywords: breast cancer; inflammation; microRNAs; regulation; ros.
Copyright © 2022 Villarreal-García, Estupiñan-Jiménez, Vivas-Mejía, Gonzalez-Villasana, Vázquez-Guillén and Reséndez-Pérez.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A cutting-edge immunomodulatory interlinkage between HOTAIR and MALAT1 in tumor-associated macrophages in breast cancer: A personalized immunotherapeutic approach.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Oct 28;9:1032517. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.1032517. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36387279 Free PMC article.
-
Abundance of reactive oxygen species (ROS) is associated with tumor aggressiveness, immune response, and worse survival in breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2022 Jul;194(2):231-241. doi: 10.1007/s10549-022-06633-0. Epub 2022 May 31. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2022. PMID: 35639264 Free PMC article.
-
The Monocyte, a Maestro in the Tumor Microenvironment (TME) of Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 7;14(21):5460. doi: 10.3390/cancers14215460. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36358879 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monocytes educated by cancer-associated fibroblasts secrete exosomal miR-181a to activate AKT signaling in breast cancer cells.J Transl Med. 2022 Dec 3;20(1):559. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03780-2. J Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36463188 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of M1/M2 Macrophage Polarization in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovitis.Front Immunol. 2022 May 19;13:867260. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.867260. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35663975 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neutrophils as key regulators of tumor microenvironment in breast cancer: a focus on N1 and N2 polarization.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2025 Apr 10;87(6):3509-3522. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000003269. eCollection 2025 Jun. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40486595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Mast Cells in the Remodeling Effects of Molecular Hydrogen on the Lung Local Tissue Microenvironment under Simulated Pulmonary Hypertension.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 13;25(20):11010. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011010. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456794 Free PMC article.
-
Clinically proven natural products against breast cancer, with mechanistic insights.Oncol Res. 2025 Jun 26;33(7):1611-1632. doi: 10.32604/or.2025.062778. eCollection 2025. Oncol Res. 2025. PMID: 40612872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticle-Based Antioxidants in Stress Signaling and Programmed Cell Death in Breast Cancer Treatment.Molecules. 2023 Jul 10;28(14):5305. doi: 10.3390/molecules28145305. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37513179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Low-power red laser and blue LED modulate telomere maintenance and length in human breast cancer cells.Lasers Med Sci. 2024 Oct 7;39(1):248. doi: 10.1007/s10103-024-04194-w. Lasers Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39370492
References
-
- American Cancer Society . Cancer facts & (022). Available at: https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/all-cancer-facts... (Accessed June 15, 2022).
-
- Ahmad A. ed. Breast cancer metastasis and drug resistance: Challenges and progress. Cham: Springer International Publishing; (2019). doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-20301-6 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

