Effect and safety of extracorporeal shockwave therapy for postherpetic neuralgia: A randomized single-blind clinical study
- PMID: 36226089
- PMCID: PMC9548589
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2022.948024
Effect and safety of extracorporeal shockwave therapy for postherpetic neuralgia: A randomized single-blind clinical study
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) for postherpetic neuralgia.
Design: Randomized single-blind clinical study.
Patients: Patients with postherpetic neuralgia.
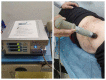
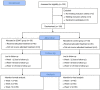
Methods: Patients were randomly divided into the control group and the ESWT group. The control group received conventional treatment while the ESWT group received conventional treatment and ESWT. The primary outcome is pain degree as assessed by the numeric rating scale (NRS), and secondary outcomes include brief pain inventory (BPI), Self-rating Anxiety Scale (SAS), Self-rating Depression Scale (SDS), and Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI). Data were collected at baseline and at weeks 1, 4, and 12. Linear mixed-effects models were applied to repeated measurement data.
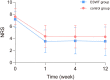
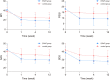
Results: The scores on the NRS, BPI, SAS, SDS, and PSQI decreased over time in both groups. The NRS and SDS scores of the ESWT group were statistically lower than the control group. There was no time × group interaction in the mixed model analysis. Baseline age was correlated with NRS scores and BPI scores, and invasive treatment was related to PSQI scores, with no interaction effect for baseline confounders observed. No adverse events were observed during the process of this trial.
Conclusion: Extracorporeal shockwave therapy combined with conventional treatment could relieve pain and improve the psychological state in patients with postherpetic neuralgia without serious adverse effects.
Keywords: chronic pain; extracorporeal shockwave therapy; neuropathic pain; postherpetic neuralgia; quality of life.
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Qing, Zhu, Yang and Ye.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Saguil A, Kane S, Mercado M, Lauters R. Herpes zoster and postherpetic neuralgia: prevention and management. Am Fam Phys. (2017) 96:656–63. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

