Particle Swarm Optimized Fuzzy CNN With Quantitative Feature Fusion for Ultrasound Image Quality Identification
- PMID: 36226132
- PMCID: PMC9550163
- DOI: 10.1109/JTEHM.2022.3197923
Particle Swarm Optimized Fuzzy CNN With Quantitative Feature Fusion for Ultrasound Image Quality Identification
Abstract
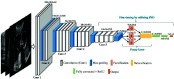
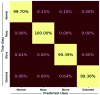
Inherently ultrasound images are susceptible to noise which leads to several image quality issues. Hence, rating of an image's quality is crucial since diagnosing diseases requires accurate and high-quality ultrasound images. This research presents an intelligent architecture to rate the quality of ultrasound images. The formulated image quality recognition approach fuses feature from a Fuzzy convolutional neural network (fuzzy CNN) and a handcrafted feature extraction method. We implement the fuzzy layer in between the last max pooling and the fully connected layer of the multiple state-of-the-art CNN models to handle the uncertainty of information. Moreover, the fuzzy CNN uses Particle swarm optimization (PSO) as an optimizer. In addition, a novel Quantitative feature extraction machine (QFEM) extracts hand-crafted features from ultrasound images. Next, the proposed method uses different classifiers to predict the image quality. The classifiers categories ultrasound images into four types (normal, noisy, blurry, and distorted) instead of binary classification into good or poor-quality images. The results of the proposed method exhibit a significant performance in accuracy (99.62%), precision (99.62%), recall (99.61%), and f1-score (99.61%). This method will assist a physician in automatically rating informative ultrasound images with steadfast operation in real-time medical diagnosis.
Keywords: Ultrasound image; feature extraction; feature fusion; fuzzy convolutional neural network; particle swarm optimization (PSO); quantitative feature extraction machine (QFEM).
Figures
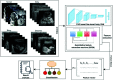
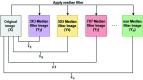
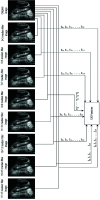
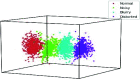

References
-
- Hughes S., “Medical ultrasound imaging,” Phys. Educ., vol. 36, no. 6, p. 468, 2001.
-
- Wang S., Zhou J., Li J., and Jiao L., “Speckle noise reduction for ultrasound images via adaptive neighborhood accumulated multi-scale products thresholding,” in Proc. Int. Conf. Intell. Sci. Intell. Data Eng. Berlin, Germany: Springer, Oct. 2011, pp. 397–404.
-
- Loizou C. P. and Pattichis C. S., “Despeckle filtering algorithms and software for ultrasound imaging,” Synth. Lectures Algorithms Softw. Eng., vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 1–166, Jan. 2008.
-
- Zhang S., Wang Y., Jiang J., Dong J., Yi W., and Hou W., “CNN-based medical ultrasound image quality assessment,” Complexity, vol. 2021, pp. 1–9, Jul. 2021.
-
- Rahman M. M., Kumar P. K. M., and Uddin M. S., “Optimum threshold parameter estimation of wavelet coefficients using Fisher discriminant analysis for speckle noise reduction,” Int. Arab J. Inf. Technol., vol. 11, no. 6, pp. 1–3, 2014.

