A Novel de novo KIF1A Mutation in a Patient with Ataxia, Intellectual Disability and Mild Foot Deformity
- PMID: 36227410
- PMCID: PMC10657280
- DOI: 10.1007/s12311-022-01489-y
A Novel de novo KIF1A Mutation in a Patient with Ataxia, Intellectual Disability and Mild Foot Deformity
Erratum in
-
Correction: A Novel de novo KIF1A Mutation in a Patient with Ataxia, Intellectual Disability and Mild Foot Deformity.Cerebellum. 2023 Dec;22(6):1312. doi: 10.1007/s12311-022-01490-5. Cerebellum. 2023. PMID: 36322330 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Early-onset ataxias are often difficult to diagnose due to the genetic and phenotypic heterogeneity of patients. Whole exome sequencing (WES) is a powerful method for determining causative mutations of early-onset ataxias. We report a case in which a novel de novo KIF1A mutation was identified in a patient with ataxia, intellectual disability and mild foot deformity.A patient presented with sporadic forms of ataxia with mild foot deformity, intellectual disability, peripheral neuropathy, pyramidal signs, and orthostatic hypotension. WES was used to identify a novel de novo mutation in KIF1A, a known causative gene of neurodegeneration and spasticity with or without cerebellar atrophy or cortical visual impairment syndrome (NESCAVS).We report a novel phenotype of NESCAVS that is associated with a novel de novo missense mutation in KIF1A, which provides valuable information for the diagnosis of NESCAVS even in the era of WES. Early rehabilitation of patients with NESCAVS may prevent symptom worsening and improve the disease course.
Keywords: Ataxia; Foot deformity; Intellectual disability; KIF1A; Whole-exome sequencing.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
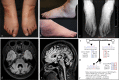
Similar articles
-
De novo KIF1A mutations cause intellectual deficit, cerebellar atrophy, lower limb spasticity and visual disturbance.J Hum Genet. 2015 Dec;60(12):739-42. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2015.108. Epub 2015 Sep 10. J Hum Genet. 2015. PMID: 26354034
-
Novel De Novo KCND3 Mutation in a Japanese Patient with Intellectual Disability, Cerebellar Ataxia, Myoclonus, and Dystonia.Cerebellum. 2018 Apr;17(2):237-242. doi: 10.1007/s12311-017-0883-4. Cerebellum. 2018. PMID: 28895081
-
Whole exome sequencing is necessary to clarify ID/DD cases with de novo copy number variants of uncertain significance: Two proof-of-concept examples.Am J Med Genet A. 2016 Jul;170(7):1772-9. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.37649. Epub 2016 Apr 25. Am J Med Genet A. 2016. PMID: 27108886
-
Report of a de novo c.2605C > T (p.Pro869Ser) change in the MED13L gene and review of the literature for MED13L-related intellectual disability.Ital J Pediatr. 2020 Jul 9;46(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s13052-020-00847-y. Ital J Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32646507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exome sequencing identifies a de novo SCN2A mutation in a patient with intractable seizures, severe intellectual disability, optic atrophy, muscular hypotonia, and brain abnormalities.Epilepsia. 2014 Apr;55(4):e25-9. doi: 10.1111/epi.12554. Epub 2014 Mar 1. Epilepsia. 2014. PMID: 24579881 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

