High frame-rate contrast enhanced ultrasound (HIFR-CEUS) in the characterization of small hepatic lesions in cirrhotic patients
- PMID: 36227456
- PMCID: PMC10063709
- DOI: 10.1007/s40477-022-00724-w
High frame-rate contrast enhanced ultrasound (HIFR-CEUS) in the characterization of small hepatic lesions in cirrhotic patients
Abstract
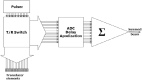
Background: To show the effectiveness of plane wave HighFrame-Rate CEUS (HiFR-CEUS) compared with "conventional" (plane wave) CEUS (C-CEUS) in the characterization of small (< 2 cm) focal liver lesions (FLLs) not easily detected by CT in cirrhotic patients. HiFR-CEUS exploit an ultra-wideband nonlinear process to combine fundamental, second and higher-order harmonic signals generated by ultrasound contrast agents to increase the frame rate. C-CEUS is limited by the transmission principle, and its frame-rate is around 10 FPS. With HiFR-CEUS (Shenzhen Mindray Bio-Medical Electronics Co., China), the frame-rate reached 60 FPS.
Material and methods: Ultrasound detected small FLLs (< 2 cm) in 63 cirrhotic patients during follow-up (June 2019-February 2020); (7 nodules < 1 cm and were not evaluable by spiral CT). Final diagnosis was obtained with MRI (47) or fine needle aspiration (16 cases) C-CEUS was performed and HiFR-CEUS was repeated after 5 min; 0.8-1.2 ml of contrast media (SonoVue, Bracco, Italy) was used. 57 nodules were better evaluable with HiFR-CEUS; 6 nodules were equally evaluable by both techniques; final diagnosis was: 44 benign lesions (29 hemangiomas, 1 amartoma, 2 hepatic cysts; 2 focal nodular hyperplasias, 3 regenerative macronodules, 3 AV-shunts, 3 hepatic sparing areas and 1 focal steatosis) and 19 malignant one (17 HCCs, 1 cholangioca, 1 metastasis); statistical evaluation for better diagnosis with X2 test (SPSS vers. 26); we used LI-RADS classification for evaluating sensitivity, specificity PPV, NPV and diagnostic accuracy of C- and HFR-CEUS. Corrispective AU-ROC were calculated.
Results: C-CEUS and HiFR-CEUS reached the same diagnosis in 29 nodules (13 nodules > 1 < 1.5 cm; 16 nodules > 1.5 < 2 cm); HiFR-CEUS reached a correct diagnosis in 32 nodules where C-CEUS was not diagnostic (6 nodules < 1 cm; 17 nodules > 1 < 1.5 cm; 9 nodules > 1.5 < 2 cm); C-CEUS was better in 2 nodules (1 < 1 cm and 1 > 1 < 1.5 cm). Some patient's (sex, BMI, age) and nodule's characteristics (liver segment, type of diagnosis, nodule's dimensions (p = 0.65)) were not correlated with better diagnosis (p ns); only better visualization (p 0.004) was correlated; C-CEUS obtained the following LI-RADS: type-1: 18 Nodules, type-2: 21; type-3: 7, type-4: 7; type-5: 8; type-M: 2; HiFR-CEUS: type-1: 38 Nodules, type-2: 2; type-3:4, type-4: 2; type-5: 15; type-M: 2; In comparison with final diagnosis: C-CEUS: TP: 17; TN: 39; FP: 5; FN:2; HIFR-CEUS: TP: 18; TN: 41; FP: 3; FN:1; C-CEUS: sens: 89.5%; Spec: 88.6%, PPV: 77.3%; NPV: 95.1%; Diagn Acc: 88.6% (AU-ROC: 0.994 ± SEAUC: 0.127; CI: 0.969-1.019); HiHFR CEUS: sens: 94.7%; Spec: 93.2%, PPV: 85.7%; NPV: 97.6%; Diagn Acc: 93.2% (AU-ROC: 0.9958 ± SEAUC: 0.106; CI: 0.975-1.017) FLL vascularization in the arterial phase was more visible with HiFR-CEUS than with C-CEUS, capturing the perfusion details in the arterial phase due to a better temporal resolution. With a better temporal resolution, the late phase could be evaluated longer with HiFR-CEUS (4 min C-CEUS vs. 5 min HiFR-CEUS).
Conclusion: Both C-CEUS and HIFR-CEUS are good non invasive imaging system for the characterization of small lesions detected during follow up of cirrhotic patients. HiFR-CEUS allowed better FLL characterization in cirrhotic patients with better temporal and spatial resolution capturing the perfusion details that cannot be easily observed with C-CEUS.
Keywords: Cirrhosis; Contrast enhanced Ultrasound; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Nodule characterization; Plane wave technology; Sonovue.
© 2022. Società Italiana di Ultrasonologia in Medicina e Biologia (SIUMB).
Conflict of interest statement
No authors have Any conflict of interest (any financial or personal relationship with a third party whose interest could be positively or negatively influenced by the article’s content).
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

