The RA-BE-REAL Multinational, Prospective, Observational Study in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Receiving Baricitinib, Targeted Synthetic, or Biologic Disease-Modifying Therapies: a 6-Month Interim Analysis
- PMID: 36227530
- PMCID: PMC9557042
- DOI: 10.1007/s40744-022-00500-6
The RA-BE-REAL Multinational, Prospective, Observational Study in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Receiving Baricitinib, Targeted Synthetic, or Biologic Disease-Modifying Therapies: a 6-Month Interim Analysis
Abstract
Introduction: RA-BE-REAL has the overall aim of defining a profile of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) starting baricitinib or any other targeted synthetic (ts) or any biologic (b) disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) for the first time, and the primary objective of estimating time until discontinuation from any cause (excluding sustained response) of the initial treatment.
Methods: RA-BE-REAL is an ongoing, prospective, observational, 36-month study in patients with RA initiating treatment with baricitinib (cohort A) or any other tsDMARD or any bDMARD (cohort B) for the first time. The primary objective is to assess the time until treatment discontinuation from any cause (excluding sustained response) at 24 months, (i.e., the rate of discontinuation of initial baricitinib or ts/bDMARD). Patient profiles of each cohort are described and compared. Post-baseline data are descriptively analyzed. This manuscript presents baseline and interim (6-month) outcomes for European patients with RA participating in the global RA-BE-REAL study.
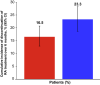
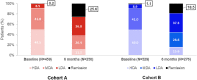
Results: Data from 1074 patients (cohort A: 509; cohort B: 565) were analyzed. For cohorts A and B, respectively, the 6-month cumulative incidence (95% confidence interval) of treatment discontinuation was 16.5 (12.9-21.1) and 23.3 (19.1-28.2), and the proportions of patients achieving remission were 25.6% and 18.5%. At baseline, mean patient age was 59.1 and 57.0 years (p = 0.010) and mean disease duration was 10.0 and 8.9 years (p = 0.047), respectively. The proportions of patients exposed to ts/bDMARDs at any time before study entry were 51.9% and 39.1%, and the proportions of patients initiated on monotherapy were 50.9% and 31.2%, respectively.
Conclusion: In real-world settings, patients with RA initiating treatment with baricitinib were older and had longer disease duration than those initiating treatment with any other tsDMARD or any bDMARD. Initial descriptive data regarding treatment discontinuation (including reasons for discontinuation), effectiveness, and treatment patterns will be enriched as the study progresses.
Keywords: Baricitinib; Effectiveness; Patient-reported outcomes; Rheumatoid arthritis; Treatment discontinuation observational study; bDMARDs; tsDMARDs.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative Effectiveness, Time to Discontinuation, and Patient-Reported Outcomes with Baricitinib in Rheumatoid Arthritis: 2-Year Data from the Multinational, Prospective Observational RA-BE-REAL Study in European Patients.Rheumatol Ther. 2023 Dec;10(6):1575-1595. doi: 10.1007/s40744-023-00597-3. Epub 2023 Sep 27. Rheumatol Ther. 2023. PMID: 37755648 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics and 6-Month Outcomes in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Initiating Infliximab Biosimilar IFX-dyyb in a Real-World Setting.Rheumatol Ther. 2024 Jun;11(3):841-853. doi: 10.1007/s40744-024-00653-6. Epub 2024 Mar 20. Rheumatol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38507187 Free PMC article.
-
Biologic and Targeted Synthetic DMARD Utilization in the United States: Adelphi Real World Disease Specific Programme for Rheumatoid Arthritis.Rheumatol Ther. 2021 Dec;8(4):1637-1649. doi: 10.1007/s40744-021-00357-1. Epub 2021 Sep 2. Rheumatol Ther. 2021. PMID: 34487340 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic Literature Review of Real-World Evidence on Baricitinib for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Rheumatol Ther. 2023 Dec;10(6):1417-1457. doi: 10.1007/s40744-023-00591-9. Epub 2023 Sep 16. Rheumatol Ther. 2023. PMID: 37715917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Singapore Chapter of Rheumatologists updated consensus statement on the eligibility for government subsidization of biologic and targeted-synthetic therapy for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.Int J Rheum Dis. 2020 Feb;23(2):140-152. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.13762. Epub 2019 Dec 19. Int J Rheum Dis. 2020. PMID: 31859424 Review.
Cited by
-
Is Baricitinib Effective and Safe for Patients with Difficult-to-Treat Rheumatoid Arthritis? Comparative Data with the Rheumatoid Arthritis Group of Rheumatoid Arthritis Not Difficult to Treat.Med Princ Pract. 2025;34(1):75-86. doi: 10.1159/000541488. Epub 2024 Sep 17. Med Princ Pract. 2025. PMID: 39288740 Free PMC article.
-
A JAK Inhibitor for Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Baricitinib Experience.J Clin Med. 2023 Jul 6;12(13):4527. doi: 10.3390/jcm12134527. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37445562 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative effectiveness of baricitinib and alternative biological DMARDs in a Swiss cohort study of patients with RA.BMJ Open. 2024 Mar 12;14(3):e072300. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-072300. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 38479734 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Effectiveness, Time to Discontinuation, and Patient-Reported Outcomes with Baricitinib in Rheumatoid Arthritis: 2-Year Data from the Multinational, Prospective Observational RA-BE-REAL Study in European Patients.Rheumatol Ther. 2023 Dec;10(6):1575-1595. doi: 10.1007/s40744-023-00597-3. Epub 2023 Sep 27. Rheumatol Ther. 2023. PMID: 37755648 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Patient-Reported Pain and Remission or Low Disease Activity in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Data from RA-BE-REAL Prospective Observational Study.Rheumatol Ther. 2025 Feb;12(1):109-122. doi: 10.1007/s40744-024-00732-8. Epub 2024 Dec 17. Rheumatol Ther. 2025. PMID: 39688792 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

