Incidence, Prevalence, and Mortality of Lupus Nephritis: A Population-Based Study Over Four Decades Using the Lupus Midwest Network
- PMID: 36227575
- PMCID: PMC10065880
- DOI: 10.1002/art.42375
Incidence, Prevalence, and Mortality of Lupus Nephritis: A Population-Based Study Over Four Decades Using the Lupus Midwest Network
Abstract
Objective: There is a paucity of population-based studies investigating the epidemiology of lupus nephritis (LN) in the US and long-term secular trends of the disease and its outcomes. We aimed to examine the epidemiology of LN in a well-defined 8-county region in the US.
Methods: Patients with incident LN between 1976 and 2018 in Olmsted County, Minnesota (1976-2009) and an 8-county region in southeast Minnesota (2010-2018) were identified. Age- and sex-specific incidence rates and point prevalence over 4 decades, adjusted to the projected 2000 US population, were determined. Standardized mortality ratios (SMRs), survival rates, and time to end-stage renal disease (ESRD) were estimated.
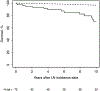
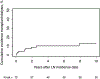
Results: There were 72 patients with incident LN between 1976 and 2018, of whom 76% were female and 69% were non-Hispanic White. Mean ± SD age at diagnosis was 38.4 ± 16.24 years. Average annual LN incidence per 100,000 population between 1976 and 2018 was 1.0 (95% CI 0.8-1.3) and was highest in patients ages 30-39 years. Between the 1976-1989 and 2000-2018 time periods, overall incidence of LN increased from 0.7 to 1.3 per 100,000, but this was not statistically significant. Estimated LN prevalence increased from 16.8 per 100,000 in 1985 to 21.2 per 100,000 in 2015. Patients with LN had an SMR of 6.33 (95% CI 3.81-9.89), with no improvement in the mortality gap in the last 4 decades. At 10 years, survival was 70%, and 13% of LN patients had ESRD.
Conclusion: The incidence and prevalence of LN in this area increased in the last 4 decades. LN patients have poor outcomes, with high rates of ESRD and mortality rates 6 times that of the general population.
© 2022 American College of Rheumatology.
Figures
References
-
- Alarcon GS. Multiethnic lupus cohorts: what have they taught us? Reumatol Clin 2011; 7(1): 3–6. - PubMed
-
- Bastian HM, Roseman JM, McGwin G Jr., et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus in three ethnic groups. XII. Risk factors for lupus nephritis after diagnosis. Lupus 2002; 11(3): 152–60. - PubMed
-
- Cervera R, Khamashta MA, Font J, et al. Morbidity and mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus during a 5-year period. A multicenter prospective study of 1,000 patients. European Working Party on Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Medicine (Baltimore) 1999; 78(3): 167–75. - PubMed
-
- Fanouriakis A, Kostopoulou M, Cheema K, et al. 2019 Update of the Joint European League Against Rheumatism and European Renal Association-European Dialysis and Transplant Association (EULAR/ERA-EDTA) recommendations for the management of lupus nephritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2020; 79(6): 713–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

