The transcription factors Foxf1 and Foxf2 integrate the SHH, HGF and TGFβ signaling pathways to drive tongue organogenesis
- PMID: 36227576
- PMCID: PMC10655918
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.200667
The transcription factors Foxf1 and Foxf2 integrate the SHH, HGF and TGFβ signaling pathways to drive tongue organogenesis
Abstract
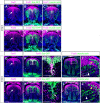
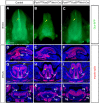
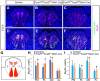
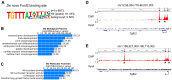
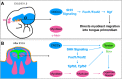
The tongue is a highly specialized muscular organ with diverse cellular origins, which provides an excellent model for understanding mechanisms controlling tissue-tissue interactions during organogenesis. Previous studies showed that SHH signaling is required for tongue morphogenesis and tongue muscle organization, but little is known about the underlying mechanisms. Here we demonstrate that the Foxf1/Foxf2 transcription factors act in the cranial neural crest cell (CNCC)-derived mandibular mesenchyme to control myoblast migration into the tongue primordium during tongue initiation, and thereafter continue to regulate intrinsic tongue muscle assembly and lingual tendon formation. We performed chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing analysis and identified Hgf, Tgfb2 and Tgfb3 among the target genes of Foxf2 in the embryonic tongue. Through genetic analyses of mice with CNCC-specific inactivation of Smo or both Foxf1 and Foxf2, we show that Foxf1 and Foxf2 mediate hedgehog signaling-mediated regulation of myoblast migration during tongue initiation and intrinsic tongue muscle formation by regulating the activation of the HGF and TGFβ signaling pathways. These data uncover the molecular network integrating the SHH, HGF and TGFβ signaling pathways in regulating tongue organogenesis.
Keywords: Gene regulatory network; Myoblast migration; Neural crest; SHH; TGFβ signaling; Tongue development.
© 2022. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sonic hedgehog signaling in craniofacial development.Differentiation. 2023 Sep-Oct;133:60-76. doi: 10.1016/j.diff.2023.07.002. Epub 2023 Jul 13. Differentiation. 2023. PMID: 37481904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Shh-Foxf-Fgf18-Shh Molecular Circuit Regulating Palate Development.PLoS Genet. 2016 Jan 8;12(1):e1005769. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005769. eCollection 2016 Jan. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 26745863 Free PMC article.
-
Sonic hedgehog regulation of Foxf2 promotes cranial neural crest mesenchyme proliferation and is disrupted in cleft lip morphogenesis.Development. 2017 Jun 1;144(11):2082-2091. doi: 10.1242/dev.149930. Epub 2017 May 15. Development. 2017. PMID: 28506991 Free PMC article.
-
A SHH-FOXF1-BMP4 signaling axis regulating growth and differentiation of epithelial and mesenchymal tissues in ureter development.PLoS Genet. 2017 Aug 10;13(8):e1006951. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006951. eCollection 2017 Aug. PLoS Genet. 2017. PMID: 28797033 Free PMC article.
-
FOXF2 acts as a crucial molecule in tumours and embryonic development.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Jun 5;11(6):424. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2604-z. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32503970 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sonic hedgehog signaling in craniofacial development.Differentiation. 2023 Sep-Oct;133:60-76. doi: 10.1016/j.diff.2023.07.002. Epub 2023 Jul 13. Differentiation. 2023. PMID: 37481904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TFAP2 paralogs regulate midfacial development in part through a conserved ALX genetic pathway.Development. 2024 Jan 1;151(1):dev202095. doi: 10.1242/dev.202095. Epub 2024 Jan 2. Development. 2024. PMID: 38063857 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the hedgehog pathway in MET mutation cancers and its effects on cells associated with cancer development.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Nov 2;21(1):313. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01333-8. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37919751 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct expression patterns of Hedgehog signaling components in mouse gustatory system during postnatal tongue development and adult homeostasis.PLoS One. 2024 Jun 7;19(6):e0294835. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0294835. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38848388 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the Forkhead box family protein FOXF2 in the progression of solid tumor: systematic review.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 Dec 26;151(1):14. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-06047-z. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39724282 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amano, O., Yamane, A., Shimada, M., Koshimizu, U., Nakamura, T. and Iseki, S. (2002). Hepatocyte growth factor is essential for migration of myogenic cells and promotes their proliferation during the early periods of tongue morphogenesis in mouse embryos. Dev. Dyn. 223, 169-179. 10.1002/dvdy.1228 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bolte, C., Ren, X., Tomley, T., Ustiyan, V., Pradhan, A., Hoggatt, A., Kalin, T. V., Herring, B. P. and Kalinichenko, V. V. (2015). Forkhead box F2 regulation of platelet-derived growth factor and myocardin/serum response factor signaling is essential for intestinal development. J. Biol. Chem. 290, 7563-7575. 10.1074/jbc.M114.609487 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

