Evaluating the Feasibility of a Digital Therapeutic Program for Patients With Cancer During Active Treatment: Pre-Post Interventional Study
- PMID: 36227639
- PMCID: PMC9614627
- DOI: 10.2196/39764
Evaluating the Feasibility of a Digital Therapeutic Program for Patients With Cancer During Active Treatment: Pre-Post Interventional Study
Abstract
Background: Increasing evidence shows that lifestyle interventions can improve the symptoms, quality of life (QoL), and even overall survival of patients with cancer. Digital therapeutics (DTx) can help implement behavioral modifications and empower patients through education, lifestyle support, and remote symptom monitoring.
Objective: We aimed to test the feasibility of a DTx program for patients with cancer, as measured by engagement, retention, and acceptability. In addition, we explored the effects of the program on cancer-related QoL.
Methods: We conducted a 4-week single-arm trial in Iceland, where DTx was delivered through a smartphone app. The intervention consisted of patient education about mindfulness, sleep, stress, and nutrition; lifestyle coaching; and the completion of daily missions for tracking physical activity and exercise, reporting patient-reported outcomes (PROs), practicing mindfulness, and logging healthy food intake. Information on program engagement and retention, step goal attainment, as well as PROs were collected throughout the study. QoL was measured using the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Questionnaire C30 at baseline and follow-up.
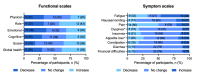
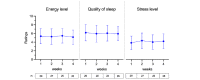
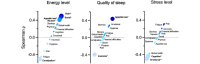
Results: In total, 30 patients with cancer undergoing active therapy were enrolled, and 29 registered in the app (23 female, 18 with breast cancer; mean age 52.6, SD 11.5 years). Overall, 97% (28/29) of participants were active in 3 of the 4 weeks and completed the pre- and postprogram questionnaires. The weekly active days (median) were 6.8 (IQR 5.8-6.8), and 72% (21/29) of participants were active at least 5 days a week. Users interacted with the app on average 7.7 (SD 1.9) times per day. On week 1, all 29 participants used the step counter and logged an average of 20,306 steps; 21 (72%) participants reached their step goals of at least 3000 steps per day. On week 4, of the 28 active users, 27 (96%) were still logging their steps, with 19 (68%) reaching their step goals. Of the 28 participants who completed the satisfaction questionnaire, 25 (89%) were likely to recommend the program, 23 (82%) said the program helped them deal with the disease, and 24 (86%) said it helped them remember their medication. QoL assessment showed that the average global health status, functioning, and symptom burden remained stable from baseline to follow-up. In all, 50% (14/28) of participants reported less pain, and the average pain score decreased from 31 (SD 20.1) to 22.6 (SD 23.2; P=.16). There was no significant change in PROs on the quality of sleep, energy, and stress levels from the first to the last week.
Conclusions: The high retention, engagement, and acceptability found in this study demonstrate that multidisciplinary DTx is feasible for patients with cancer. A longer, full-scale randomized controlled trial is currently being planned to evaluate the efficacy of the intervention.
Keywords: cancer; digital therapeutics; lifestyle; mobile app; mobile phone; physical activity; quality of life; self-management.
©G Haukur Gudmundsson, Judit Mészáros, Ágústa E Björnsdóttir, María L Ámundadóttir, Gudrun E Thorvardardottir, Erna Magnusdottir, Halla Helgadottir, Saemundur Oddsson. Originally published in JMIR Formative Research (https://formative.jmir.org), 13.10.2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: GHG, JM, ÁB, MLÁ, and HH are employees of Sidekick Health; in addition, SO is the cofounder of Sidekick Health.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Engagement, Retention, and Acceptability in a Digital Health Program for Atopic Dermatitis: Prospective Interventional Study.JMIR Form Res. 2023 Jun 14;7:e41227. doi: 10.2196/41227. JMIR Form Res. 2023. PMID: 36975050 Free PMC article.
-
User Engagement, Acceptability, and Clinical Markers in a Digital Health Program for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Prospective, Single-Arm Feasibility Study.JMIR Cardio. 2024 Feb 15;8:e52576. doi: 10.2196/52576. JMIR Cardio. 2024. PMID: 38152892 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating a New Digital App-Based Program for Heart Health: Feasibility and Acceptability Pilot Study.JMIR Form Res. 2024 May 24;8:e50446. doi: 10.2196/50446. JMIR Form Res. 2024. PMID: 38787598 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Need and Benefits of Digital Therapeutics (DTx) for the Management of Heart Failure in India.Cureus. 2023 Nov 29;15(11):e49628. doi: 10.7759/cureus.49628. eCollection 2023 Nov. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38161874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Developing & integrating a mobile application tool into a survivorship clinic for esophageal cancer patients.J Thorac Dis. 2023 Apr 28;15(4):2240-2252. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-1343. Epub 2023 Apr 25. J Thorac Dis. 2023. PMID: 37197528 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Digital innovations in breast cancer care: exploring the potential and challenges of digital therapeutics and clinical decision support systems.Digit Health. 2024 Nov 3;10:20552076241288821. doi: 10.1177/20552076241288821. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Digit Health. 2024. PMID: 39502478 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mobile apps for cancer patients: Identifying positive impacts and concerns.Digit Health. 2025 Mar 3;11:20552076241305707. doi: 10.1177/20552076241305707. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. Digit Health. 2025. PMID: 40041393 Free PMC article.
-
Digital therapeutics and its role in cancer treatment management: current development and future scope.Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2024 Jul 19;70(6):e20240183. doi: 10.1590/1806-9282.20240183. eCollection 2024. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2024. PMID: 39045968 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Development and Implementation of an eHealth Oncohematonootric Program: Descriptive, Observational, Prospective Cohort Pilot Study.JMIR Form Res. 2024 Apr 8;8:e49574. doi: 10.2196/49574. JMIR Form Res. 2024. PMID: 38588522 Free PMC article.
-
A Digital Program for Daily Life Management With Endometriosis: Pilot Cohort Study on Symptoms and Quality of Life Among Participants.JMIR Form Res. 2025 Feb 28;9:e58262. doi: 10.2196/58262. JMIR Form Res. 2025. PMID: 39791286 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021 May;71(3):209–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660. - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aðalvalmynd. Krabbameinsfélagið. [2022-02-08]. https://www.krabb.is/rannsoknasetur/upplysingar-um-krabbamein/yfirlitsto...
-
- Zoberi K, Tucker J. Primary care of breast cancer survivors. Am Fam Physician. 2019 Mar 15;99(6):370–5. https://www.aafp.org/link_out?pmid=30874405 d14197 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

