Coronary bioresorbable stents: Non-invasive quantitative evaluation of intra- and juxta-stent plaque composition-A computed tomography longitudinal study
- PMID: 36227938
- PMCID: PMC9560491
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0268456
Coronary bioresorbable stents: Non-invasive quantitative evaluation of intra- and juxta-stent plaque composition-A computed tomography longitudinal study
Abstract
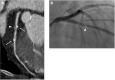
Purpose: Coronary bioresorbable stents (BRS) do not produce blooming artifacts on computed tomography (CT), in contrast to metallic stents, as they are made of a bioresorbable polymer and are radiolucent. They allow to evaluate the coronary plaque beneath. The low-attenuation plaque (LAP) suggests plaque vulnerability and is CT assessable. The aim of our study was to show the possibility of a non-invasive CT evaluation of the volume and the LAP composition of the intra- and juxta-stent plaque.
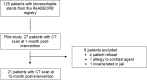
Methodology: In our prospective longitudinal study, we recruited 27 consecutive patients (35 BRS stents total; mean age 60 +/- 9 years) with bioresorbable stents for a 256-slice ECG-synchronized CT evaluation at 1- and 12-months post stent implantation. Total plaque volume (mm3), absolute and relative (%) LAP volume per block in the pre- intra- and post-stent zones were analyzed; comparison 1- and 12-months post-implantation of BRS. Changes in the previously mentioned variables were assessed by the mixed effects models with and without spline, which also accounted for the correlation between repeated measurements.
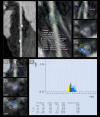
Results: Our block or spline model analysis has shown no significant difference in plaque or absolute LAP volumes in pre- intra- and post-stent zones between 1 and 12 months. Interestingly, % LAP volume increases near-significantly in the distal block of the intrastent at 12-mo follow-up (from 23.38 ± 1.80% to 26.90 ± 2.22% (increase of 15%), p = 0.052).
Conclusion: Our study demonstrates the feasibility of the repeated non-invasive quantitative analysis of the intrastent coronary plaque and of the in-stent lumen by CT scan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Brie D, Penson P, Serban M-C, Toth PP, Simonton C, Serruys PW, et al.. Bioresorbable scaffold—A magic bullet for the treatment of coronary artery disease? Int. J. Cardiol. 215, 47–59 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Ormiston JA, Serruys PW, Regar E, Dudek D, Thuesen L, Webster MWI, et al.. A bioabsorbable everolimus-eluting coronary stent system for patients with single de-novo coronary artery lesions (ABSORB): a prospective open-label trial. Lancet. 2008;371:899–907. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60415-8 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

