NSAIDs affect dendritic cell cytokine production
- PMID: 36227963
- PMCID: PMC9560552
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0275906
NSAIDs affect dendritic cell cytokine production
Abstract
Background: Immunotherapy is now considered as the new pillar in treatment of cancer patients. Dendritic cells (DCs) play an essential role in stimulating anti-tumor immune responses, as they are capable of cross-presenting exogenous tumor antigens in MHCI complexes to activate naïve CD8+ T cells. Analgesics, like non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), are frequently given to cancer patients to help relieve pain, however little is known about their impact on DC function.
Methods: Here, we investigated the effect of the NSAIDs diclofenac, ibuprofen and celecoxib on the three key processes of DCs required for proper CD8+ cytotoxic T cell induction: antigen cross-presentation, co-stimulatory marker expression, and cytokine production.
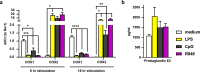
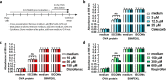
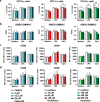
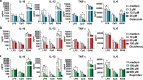
Results: Our results show that TLR-induced pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine excretion by human monocyte derived and murine bone-marrow derived DCs is diminished after NSAID exposure.
Conclusions: These results indicate that various NSAIDs can affect DC function and warrant further investigation into the impact of NSAIDs on DC priming of T cells and cancer immunotherapy efficacy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- WebMD. Pain Management: Cancer Pain. Available from: https://www.webmd.com/cancer/pain-management-cancer-pain#1.
-
- Society AC. Non-opioids and Other Drugs Used to Treat Cancer Pain [Available from: https://www.cancer.org/treatment/treatments-and-side-effects/physical-si....
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

