Targeting fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 36228471
- PMCID: PMC9942784
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coph.2022.102304
Targeting fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
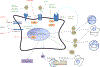
Fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) are mesenchymal-derived cells that play an important role in the physiology of the synovium by producing certain components of the synovial fluid and articular cartilage. In rheumatoid arthritis (RA), however, fibroblasts become a key driver of synovial inflammation and joint damage. Because of this, there has been recent interest in FLS as a therapeutic target in RA to avoid side effects such as systemic immune suppression associated with many existing RA treatments. In this review, we describe how approved treatments for RA affect FLS signaling and function and discuss the effects of investigational FLS-targeted drugs for RA.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement Dr. Firestein funding includes the NIH RO1 AR071321, the Allen Institute of Immunology, and Eli Lilly, Inc. Dr. Tsaltskan has no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hunter TM, Boytsov NN, Zhang X, Schroeder K, Michaud K, Araujo AB: Prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in the United States adult population in healthcare claims databases, 2004–2014. Rheumatol Int 2017, 37:1551–1557. - PubMed
-
- Smolen JS, Aletaha D, McInnes IB: Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2016, 388:2023–2038. - PubMed
-
- Feldmann M, Maini R: Perspectives From Masters in Rheumatology and Autoimmunity: Can We Get Closer to a Cure for Rheumatoid Arthritis? Arthritis Rheumatol 2015, 67. - PubMed
-
- Aletaha D, Smolen JS: Diagnosis and Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Review. JAMA 2018, 320:1360–1372. - PubMed

