Synthesis and biomedical applications of mucin mimic materials
- PMID: 36228896
- PMCID: PMC10066857
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addr.2022.114540
Synthesis and biomedical applications of mucin mimic materials
Abstract
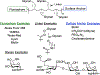
Mucin glycoproteins are the major component of mucus and coat epithelial cell surfaces forming the glycocalyx. The glycocalyx and mucus are involved in the transport of nutrients, drugs, gases, and pathogens toward the cell surface. Mucins are also involved in diverse diseases such as cystic fibrosis and cancer. Due to inherent heterogeneity in native mucin structure, many synthetic materials have been designed to probe mucin chemistry, biology, and physics. Such materials include various glycopolymers, low molecular weight glycopeptides, glycopolypeptides, polysaccharides, and polysaccharide-protein conjugates. This review highlights advances in the area of design and synthesis of mucin mimic materials, and their biomedical applications in glycan binding, epithelial models of infection, therapeutic delivery, vaccine formulation, and beyond.
Keywords: Glycopolymer; Glycopolypeptide; Mucin; Mucus.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


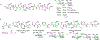
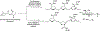
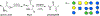
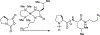
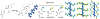
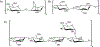
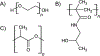

References
-
- Cone RA, Barrier properties of mucus, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 61 (2009) 75–85. - PubMed
-
- Bansil R, Turner BS, Mucin structure, aggregation, physiological functions and biomedical applications, Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 11 (2006) 164–170.
-
- Shogren R, Gerken TA, Jentoft N, Role of Glycosylation on the Conformation and Chain Dimensions of O-Linked Glycoproteins: Light-Scattering Studies of Ovine Submaxillary Mucin, Biochemistry 28 (1989) 5525–5536. - PubMed
-
- Bansil R, Mucin Biophysics, Annu. Rev. Physiol. 57 (1995) 635–657. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

