Mitofusin-2 mediates cannabidiol-induced neuroprotection against cerebral ischemia in rats
- PMID: 36229600
- PMCID: PMC9958179
- DOI: 10.1038/s41401-022-01004-3
Mitofusin-2 mediates cannabidiol-induced neuroprotection against cerebral ischemia in rats
Abstract
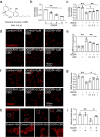
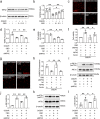
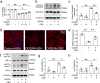
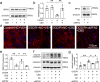
Cannabidiol (CBD) reportedly exerts protective effects against many psychiatric disorders and neurodegenerative diseases, but the mechanisms are poorly understood. In this study, we explored the molecular mechanism of CBD against cerebral ischemia. HT-22 cells or primary cortical neurons were subjected to oxygen-glucose deprivation insult followed by reoxygenation (OGD/R). In both HT-22 cells and primary cortical neurons, CBD pretreatment (0.1, 0.3, 1 μM) dose-dependently attenuated OGD/R-induced cell death and mitochondrial dysfunction, ameliorated OGD/R-induced endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, and increased the mitofusin-2 (MFN2) protein level in HT-22 cells and primary cortical neurons. Knockdown of MFN2 abolished the protective effects of CBD. CBD pretreatment also suppressed OGD/R-induced binding of Parkin to MFN2 and subsequent ubiquitination of MFN2. Overexpression of Parkin blocked the effects of CBD in reducing MFN2 ubiquitination and reduced cell viability, whereas overexpressing MFN2 abolished Parkin's detrimental effects. In vivo experiments were conducted on male rats subjected to middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) insult, and administration of CBD (2.5, 5 mg · kg-1, i.p.) dose-dependently reduced the infarct volume and ER stress in the brains. Moreover, the level of MFN2 within the ischemic penumbra of rats was increased by CBD treatment, while the binding of Parkin to MFN2 and the ubiquitination of MFN2 was decreased. Finally, short hairpin RNA against MFN2 reversed CBD's protective effects. Together, these results demonstrate that CBD protects brain neurons against cerebral ischemia by reducing MFN2 degradation via disrupting Parkin's binding to MFN2, indicating that MFN2 is a potential target for the treatment of cerebral ischemia.
Keywords: MFN2; Parkin; cannabidiol; cerebral ischemia; oxidative stress.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Chinese Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Phelligridimer A enhances the expression of mitofusin 2 and protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury.Chem Biol Interact. 2024 Aug 1;398:111090. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2024.111090. Epub 2024 May 31. Chem Biol Interact. 2024. PMID: 38825057
-
Suppression of NADPH oxidase- and mitochondrion-derived superoxide by Notoginsenoside R1 protects against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through estrogen receptor-dependent activation of Akt/Nrf2 pathways.Free Radic Res. 2014 Jul;48(7):823-38. doi: 10.3109/10715762.2014.911853. Epub 2014 May 7. Free Radic Res. 2014. PMID: 24720662
-
Rhein attenuates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via inhibition of ferroptosis through NRF2/SLC7A11/GPX4 pathway.Exp Neurol. 2023 Nov;369:114541. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2023.114541. Epub 2023 Sep 14. Exp Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37714424
-
Cannabidiol in experimental cerebral ischemia.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2024;177:95-120. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2024.04.012. Epub 2024 Jul 9. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 39029992 Review.
-
Regulatory Effects of Cannabidiol on Mitochondrial Functions: A Review.Cells. 2021 May 19;10(5):1251. doi: 10.3390/cells10051251. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34069407 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Improves Chronic Ischemic Hippocampal Damage Associated with Suppression of IRE1α/TRAF2/ASK1/JNK-Dependent Apoptosis.Inflammation. 2024 Aug;47(4):1479-1490. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-01989-5. Epub 2024 Feb 24. Inflammation. 2024. PMID: 38401021 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Polymer-Based Cannabidiol Formulation: Tackling Neuroinflammation Associated with Ischemic Events in the Brain.Mol Pharm. 2024 Apr 1;21(4):1609-1624. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.3c00244. Epub 2024 Feb 27. Mol Pharm. 2024. PMID: 38412451 Free PMC article.
-
N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor elicits a neuroprotection against ischemic neuronal injury by restoring autophagic/lysosomal dysfunction.Cell Death Discov. 2024 Aug 18;10(1):368. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-02144-7. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 39155286 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-oxidant effects of cannabidiol relevant to intracerebral hemorrhage.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Sep 28;14:1247550. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1247550. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37841923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of USP30 Promotes Mitophagy by Regulating Ubiquitination of MFN2 by Parkin to Attenuate Early Brain Injury After SAH.Transl Stroke Res. 2025 Apr;16(2):448-466. doi: 10.1007/s12975-023-01228-3. Epub 2023 Dec 26. Transl Stroke Res. 2025. PMID: 38147294 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

