Sleep postures monitoring based on capacitively coupled electrodes and deep recurrent neural networks
- PMID: 36229851
- PMCID: PMC9563454
- DOI: 10.1186/s12938-022-01031-5
Sleep postures monitoring based on capacitively coupled electrodes and deep recurrent neural networks
Abstract
Background: Capacitively coupled electrode (CC electrode), as a non-contact and unobtrusive technology for measuring physiological signals, has been widely applied in sleep monitoring scenarios. The most common implementation is capacitive electrocardiogram (cECG) that could provide useful clinical information for assessing cardiac function and detecting cardiovascular diseases. In the current study, we sought to explore another potential application of cECG in sleep monitoring, i.e., sleep postures recognition.
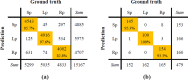
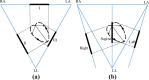
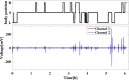
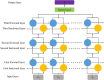
Methods: Two sets of experiments, the short-term experiment, and the overnight experiment, were conducted. The cECG signals were measured by a smart mattress based on flexible CC electrodes and sleep postures were recorded simultaneously. Then, a classifier model based on a deep recurrent neural network (RNN) was proposed to distinguish sleep postures (supine, left lateral and right lateral). To verify the reliability of the proposed model, leave-one-subject-out cross-validation was introduced.
Results: In the short-term experiment, the overall accuracy of 96.2% was achieved based on 30-s segment, while the overall accuracy was 88.8% using one heart beat segment. For the unconstrained overnight experiment, the accuracy of 91.0% was achieved based on 30-s segment, while the accuracy was 81.4% using one heart beat segment.
Conclusions: The results suggest that cECG could render valuable information about sleep postures detection and potentially be helpful for sleep disorder diagnosis.
Keywords: Capacitive electrocardiogram; Capacitively coupled electrode; Recurrent neural network; Sleep posture.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Estimation of body postures on bed using unconstrained ECG measurements.IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2013 Nov;17(6):985-93. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2013.2252911. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2013. PMID: 24240716
-
Electrocardiogram measurement during sleep with wearing clothes using capacitively-coupled electrodes.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2007;2007:2647-50. doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.2007.4352873. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2007. PMID: 18002539
-
A Novel CNN-Based Framework for Classification of Signal Quality and Sleep Position from a Capacitive ECG Measurement.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Apr 11;19(7):1731. doi: 10.3390/s19071731. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30978955 Free PMC article.
-
Stress Level Detection Based on the Capacitive Electrocardiogram Signals of Driving Subjects.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Nov 14;23(22):9158. doi: 10.3390/s23229158. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38005545 Free PMC article.
-
Contact-free sensor signals as a new digital biomarker for cardiovascular disease: chances and challenges.Eur Heart J Digit Health. 2020 Nov 27;1(1):30-39. doi: 10.1093/ehjdh/ztaa006. eCollection 2020 Nov. Eur Heart J Digit Health. 2020. PMID: 36713967 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Peng S, Bao S, Chen W. Capacitive coupled electrodes based non-contact ECG measurement system with real-time wavelet denoising algorithm. In 2019 41st annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society (EMBC), 2019, pp. 6587–6590. - PubMed
-
- Baek HJ, Kim JS, Kim KK, and Park KS. System for unconstrained ECG measurement on a toilet seat using capacitive coupled electrodes: The efficacy and practicality. In 2008 30th annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society, 2008, pp. 2326–2328 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

