The Crucial Role of AR-V7 in Enzalutamide-Resistance of Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 36230800
- PMCID: PMC9563243
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14194877
The Crucial Role of AR-V7 in Enzalutamide-Resistance of Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
Abstract
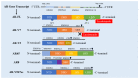
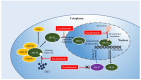
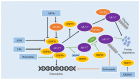
Prostate cancer (PCa) has the second highest incidence of malignancies occurring in men worldwide. The first-line therapy of PCa is androgen deprivation therapy (ADT). Nonetheless, most patients progress to castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) after being treated by ADT. As a second-generation androgen receptor (AR) antagonist, enzalutamide (ENZ) is the current mainstay of new endocrine therapies for CRPC in clinical use. However, almost all patients develop resistance during AR antagonist therapy due to various mechanisms. At present, ENZ resistance (ENZR) has become challenging in the clinical treatment of CRPC. AR splice variant 7 (AR-V7) refers to a ligand-independent and constitutively active variant of the AR and is considered a key driver of ENZR in CRPC. In this review, we summarize the mechanisms and biological behaviors of AR-V7 in ENZR of CRPC to contribute novel insights for CRPC therapy.
Keywords: AR-V7; LncRNA; castration-resistant prostate cancer; drug resistance; enzalutamide; proteostasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Cornford P., Bellmunt J., Bolla M., Briers E., De Santis M., Gross T., Henry A.M., Joniau S., Lam T.B., Mason M.D., et al. EAU-ESTRO-SIOG Guidelines on Prostate Cancer. Part II: Treatment of Relapsing, Metastatic, and Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2017;71:630–642. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.08.002. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

