Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Molecular Pathology and Predictive Biomarkers
- PMID: 36231030
- PMCID: PMC9563270
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11193068
Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Molecular Pathology and Predictive Biomarkers
Abstract
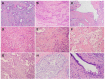
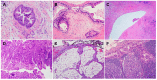
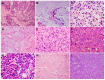
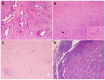
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) has an extremely poor prognosis due to the lack of methods or biomarkers for early diagnosis and its resistance to conventional treatment modalities, targeted therapies, and immunotherapies. PDACs are a heterogenous group of malignant epithelial neoplasms with various histomorphological patterns and complex, heterogenous genetic/molecular landscapes. The newly proposed molecular classifications of PDAC based on extensive genomic, transcriptomic, proteomic and epigenetic data have provided significant insights into the molecular heterogeneity and aggressive biology of this deadly disease. Recent studies characterizing the tumor microenvironment (TME) have shed light on the dynamic interplays between the tumor cells and the immunosuppressive TME of PDAC, which is essential to disease progression, as well as its resistance to chemotherapy, newly developed targeted therapy and immunotherapy. There is a critical need for the development of predictive markers that can be clinically utilized to select effective personalized therapies for PDAC patients. In this review, we provide an overview of the histological and molecular heterogeneity and subtypes of PDAC, as well as its precursor lesions, immunosuppressive TME, and currently available predictive molecular markers for patients.
Keywords: molecular pathology; pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; predictive marker; targeted therapy and immunotherapy; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest related to this publication.
Figures
References
-
- National Cancer Institute SRP, Cancer Statistics Branch Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) (1975–2018) [(accessed on 7 August 2022)];2021 Available online: http://seer.cancer.gov.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

