Climate Changes, Natural Resources Depletion, COVID-19 Pandemic, and Russian-Ukrainian War: What Is the Impact on Habits Change and Mental Health?
- PMID: 36231229
- PMCID: PMC9565033
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph191911929
Climate Changes, Natural Resources Depletion, COVID-19 Pandemic, and Russian-Ukrainian War: What Is the Impact on Habits Change and Mental Health?
Abstract
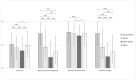
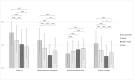
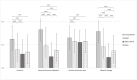
Climate Change, Natural Resources Depletion, COVID-19, and Wars are some of the great challenges of our time. The consequences will affect psychological well-being and could have a harmful impact on mental health. This study aimed to assess the level of preoccupation and fears surrounding issues of the 21st-century and the implication for psychological well-being of the general population from Central/Southern Italy among different age groups. A questionnaire that included sociodemographic characteristics, topics formulated ad-hoc about preoccupation, fears, habits, and willingness to change habits in the future related to the 21st-century challenges, and the Depression Anxiety Stress Scales 21 (DASS-21) was administered online. A sample of 1831 participants (61% F; mean age 47.71 ± 17.30) was obtained. Results showed that young adults and older adults, respectively, reported greater and less psychological well-being. Young adults reported higher scores for preoccupation, changing habits, and willingness to change habits in the future, while older adults reported the lowest scores except for changing habits, also controlling for gender. Results for this variable, as well as correlations between the many variables described, rely on the specificity of age, and 21st-century challenges. Moreover, the main fears related to the 21st-century concerns were different based on both age and gender. In conclusion, the various stresses of the 21st-century discussed in this study have a relationship with personal well-being, and it is important to consider potential global mental health issues resulting from these stressors.
Keywords: COVID-19 pandemic; Climate Changes; Natural Resources Depletion; Russian-Ukrainian War; psychological well-being.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Pasimeni M.R., Valente D., Zurlini G., Petrosillo I. The interplay between urban mitigation and adaptation strategies to face climate change in two European countries. Environ. Sci. Policy. 2019;95:20–27. doi: 10.1016/j.envsci.2019.02.002. - DOI
-
- Ghinoi S., Steiner B. The Political Debate on Climate Change in Italy: A Discourse Network Analysis. Politics Gov. 2020;8:215–228. doi: 10.17645/pag.v8i2.2577. - DOI
-
- Forestieri A., Arnone E., Blenkinsop S., Candela A., Fowler H., Noto L.V. The impact of climate change on extreme precipitation in Sicily, Italy. Hydrol. Process. 2018;32:332–348. doi: 10.1002/hyp.11421. - DOI
-
- Chelli S., Wellstein C., Campetella G., Canullo R., Tonin R., Zerbe S., Gerdol R. Climate change response of vegetation across climatic zones in Italy. Clim. Res. 2017;71:249–262. doi: 10.3354/cr01443. - DOI
-
- Galeotti M., Roson R. Economic Impacts of Climate Change in Italy and the Mediterranean: Updating the Evidence. J. Sustain. Dev. 2012;5:27. doi: 10.5539/jsd.v5n5p27. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

