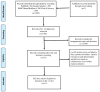
Global Cross-Border Malaria Control Collaborative Initiatives: A Scoping Review
- PMID: 36231519
- PMCID: PMC9566216
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph191912216
Global Cross-Border Malaria Control Collaborative Initiatives: A Scoping Review
Abstract
Malaria remains a global disease of public health concern. Malaria control collaborative initiatives are widely being adopted to reduce malaria burden by various countries. This review sought to describe current and past cross-border malaria control initiatives focusing on key activities, outcomes and challenges. An exhaustive search was conducted in Web of Science, PubMed, Google Scholar and EBSCOhost using the following key words: cross-border malaria control, cross-border malaria elimination, bi-national malaria control and multinational malaria control, in combination with Boolean operators "AND" and "OR". Eleven studies satisfied the inclusion criteria for this review. The majority of collaborative initiatives have been formed within regional developmental and continental bodies with support from political leadership. The studies revealed that joint vector control, cases management, epidemiological data sharing along border regions as well as resource sharing and capacity building are some of the key collaborative initiatives being implemented globally. Collaborative initiatives have led to significant reduction in malaria burden and mortality. The majority of collaborative initiatives are underfunded and rely on donor support. We concluded that cross-border malaria collaborative initiatives have the capacity to reduce malaria burden and mortality along border regions; however, inadequate internal funding and over-reliance on donor funding remain the biggest threats to the survival of collaborative initiatives.
Keywords: border malaria control; cross-border malaria; malaria collaborative initiatives.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organisation World Malaria Report 2021. 2022. [(accessed on 22 February 2022)]. Available online: https://wwwwhoint/publications/i/item/9789240040496.
-
- World Health Organization . World Malaria Report 2020: 20 Years of Global Progress and Challenges. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2020.
-
- Nabarro D.N., Tayler E.M. The “Roll Back Malaria” Campaign. American Association for the Advancement of Science; Washington, DC, USA: 1998. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous