Factors That Affect the COVID-19 Pandemic in Summer 2022 Compared to Summer 2021
- PMID: 36231856
- PMCID: PMC9566291
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph191912561
Factors That Affect the COVID-19 Pandemic in Summer 2022 Compared to Summer 2021
Abstract
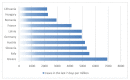
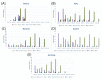
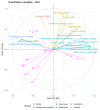
The COVID-19 pandemic still goes on. The increasing number of COVID-19 cases has been observed since the start of summer 2022, although this was not in summer 2021. Therefore, we would like to compare factors that were responsible for this trend in five selected countries in the European Union (Greece, Italy, Slovenia, Austria and Germany) using the data from publicly available databases for the analyzed period of weeks 22-30 in 2021 and 2022. The multiple factor analysis was conducted in R, using mean or median score. Our cross-sectional study showed that analyzed countries had similar profiles in 2021 characterized by restrictions and health system policies, as well as B.1.351, B.1.1.7, B.1.617.2 and P.1 variants. Similarly, these countries had similar profiles in 2022, but described by other variables: number of new COVID-19 cases per million, number people fully vaccinated per hundred, number of total boosters administered per hundred and also occurrence of Omicron variant and its sub-lineages. Although the COVID-19 vaccination rate is relatively high in the European Union, during the summer of 2022, the number of COVID-19 cases sharply increased daily, which seems to be connected with the presence of the Omicron variant and its sub-lineages.
Keywords: COVID-19; Omicron; SARS-CoV-2; multiple factor analysis; restrictions; vaccination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Cardwell K., O’Neill S.M., Tyner B., Broderick N., O’Brien K., Smith S.M., Harrington P., Ryan M., O’Neill M. A Rapid Review of Measures to Support People in Isolation or Quarantine during the COVID-19 Pandemic and the Effectiveness of Such Measures. Rev. Med. Virol. 2022;32:e2244. doi: 10.1002/rmv.2244. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jiang S., Wu S., Zhao G., He Y., Bao L., Liu J., Qin C., Hou J., Ding Y., Cheng A., et al. Comparison of Wild Type DNA Sequence of Spike Protein from SARS-CoV-2 with Optimized Sequence on The Induction of Protective Responses Against SARS-CoV-2 Challenge in Mouse Model. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2022;18:2016201. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2021.2016201. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

