Association of Parental Screen Addiction with Young Children's Screen Addiction: A Chain-Mediating Model
- PMID: 36232109
- PMCID: PMC9566204
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph191912788
Association of Parental Screen Addiction with Young Children's Screen Addiction: A Chain-Mediating Model
Abstract
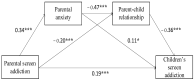
Preschool children are immersed in screen media, yet little study has been conducted on screen addiction among them. This study aimed to investigate the relationship between parental screen addiction and young children's screen addiction and to verify factors that mediate this relationship. A total of 477 parents of kindergarteners (3-6 years old) were recruited via six kindergartens in Henan province, China. They completed the Problematic Media Use Measure Short Form of Children, the Self-Rating Anxiety Scale, the Child-Parent Relationship Scale, and the Parental Screen Addiction Scale. The results showed that the relationships between each pair of parental screen addiction, parental anxiety, and children's screen addiction were significantly positive, but the parent-child relationship was negatively correlated with the other variables. Parental screen addiction can directly and indirectly affect children's screen addiction through parental anxiety and the parent-child relationship. The findings contribute to the development of family protection mechanisms against screen addiction in children.
Keywords: children’s screen addiction; parental anxiety; parental screen addiction; parent–child relationship.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effects of parental marital quality on preschool children's social-emotional competence: The chain mediating model of parent-child and sibling relationships.Infant Ment Health J. 2025 Jan;46(1):15-29. doi: 10.1002/imhj.22148. Epub 2024 Nov 29. Infant Ment Health J. 2025. PMID: 39611600
-
The Chain Mediating Effects of Parent-Child Conflict and Screen Time on the Relationship Between Parental Phubbing and Problem Behaviors in Preschoolers.Behav Sci (Basel). 2025 Feb 13;15(2):203. doi: 10.3390/bs15020203. Behav Sci (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40001835 Free PMC article.
-
[The Influence of Parental Self-Esteem on Late School-Aged Children's Media Device Addiction: The Mediating Effect of Marital Conflict and Children's Self-Esteem].J Korean Acad Nurs. 2022 Aug;52(4):421-434. doi: 10.4040/jkan.22036. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2022. PMID: 36117303 Korean.
-
Parental Educational Anxiety during Children's Transition to Primary School in China.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Nov 22;19(23):15479. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192315479. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36497552 Free PMC article.
-
Advancing Research on Mobile Screen Media and Young Children's Cognitive Skills.Acad Pediatr. 2025 Jan-Feb;25(1):102531. doi: 10.1016/j.acap.2024.06.018. Epub 2024 Jul 4. Acad Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 38971521 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Problematic Digital Technology Use Measures in Children Aged 0 to 6 Years: Scoping Review.JMIR Ment Health. 2025 Mar 18;12:e59869. doi: 10.2196/59869. JMIR Ment Health. 2025. PMID: 40100254 Free PMC article.
-
A Scoping Review of Digital Well-Being in Early Childhood: Definitions, Measurements, Contributors, and Interventions.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Feb 16;20(4):3510. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20043510. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36834204 Free PMC article.
-
Emotional Reactivity and Behavioral Problems in Preschoolers: The Interplay of Parental Stress, Media-Related Coping, and Child Screen Time.Children (Basel). 2025 Feb 5;12(2):188. doi: 10.3390/children12020188. Children (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40003290 Free PMC article.
-
Internet gaming disorder (IGD) and smartphone addiction: parent intervention trial.Aust J Psychol. 2024 Sep 8;76(1):2396961. doi: 10.1080/00049530.2024.2396961. eCollection 2024. Aust J Psychol. 2024. PMID: 40666642 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship Between Speech Delay and Smart Media in Children: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2023 Sep 17;15(9):e45396. doi: 10.7759/cureus.45396. eCollection 2023 Sep. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37854747 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bölükbaşı Macit Z., Kavafoğlu S. Screen: Subject of all Information Technology Addiction. Middle Black Sea J. Health Sci. 2019;5:293–301. doi: 10.19127/mbsjohs.542122. - DOI
-
- Carrier L.M., Rosen L.D., Cheever N.A., Lim A.F. Causes, effects, and practicalities of everyday multitasking. Dev. Rev. 2015;35:64–78. doi: 10.1016/j.dr.2014.12.005. - DOI
-
- Li W., Liu A. The quantity and quality of screen exposure and preschool children’s non-cognitive skill. J. Educ. Stud. 2022;18:99–112. doi: 10.14082/j.cnki.1673-1298.2022.01.011. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources