Have Deaths of Despair Risen during the COVID-19 Pandemic? A Systematic Review
- PMID: 36232135
- PMCID: PMC9564909
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph191912835
Have Deaths of Despair Risen during the COVID-19 Pandemic? A Systematic Review
Abstract
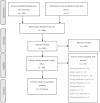
This systematic review synthesized literature on potential impacts of protracted isolation and other disruptions during the COVID-19 pandemic on deaths of despair (suicide, overdoses, and drug-related liver diseases). Five electronic databases were searched yielding 70 eligible articles. Extant evidence mostly from high-income countries indicates COVID-19-related disruption may not have influenced suicide rates so far, but there have been reports of increased drug-related and liver disease mortality. Minority groups and women were more vulnerable, indicating the need for stronger equity focus on pandemic recovery and resilience strategies. Further high-quality studies with longer-term follow-up, especially from low-income countries, will inform these strategies.
Keywords: COVID-19; deaths of despair; overdose; suicide; systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Santomauro D.F., Mantilla Herrera A.M., Shadid J., Zheng P., Ashbaugh C., Pigott D.M., Abbafati C., Adolph C., Amlag J.O., Aravkin A.Y., et al. Global prevalence and burden of depressive and anxiety disorders in 204 countries and territories in 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet. 2021;398:1700–1712. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02143-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Phiri P., Ramakrishnan R., Rathod S., Elliot K., Thayanandan T., Sandle N., Haque N., Chau S.W.H., Wong O.W.H., Chan S.S.M., et al. An evaluation of the mental health impact of SARS-CoV-2 on patients, general public and healthcare professionals: A systematic review and meta-analysis. eClinicalMedicine. 2021;34:100806. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100806. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- John A., Eyles E., Webb R.T., Okolie C., Schmidt L., Arensman E., Hawton K., O’Connor R.C., Kapur N., Moran P., et al. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on self-harm and suicidal behaviour: Update of living systematic review. F1000Research. 2020;9:1097. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.25522.1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rogers J.P., Chesney E., Oliver D., Begum N., Saini A., Wang S., McGuire P., Fusar-Poli P., Lewis G., David A.S. Suicide, self-harm and thoughts of suicide or self-harm in infectious disease epidemics: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Epidemiol. Psychiatr. Sci. 2021;30:e32. doi: 10.1017/S2045796021000214. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Imtiaz S., Nafeh F., Russell C., Ali F., Elton-Marshall T., Rehm J. The impact of the novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic on drug overdose-related deaths in the United States and Canada: A systematic review of observational studies and analysis of public health surveillance data. Subst. Abuse Treat. Prev. Policy. 2021;16:87. doi: 10.1186/s13011-021-00423-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical