Factors Related to the Intention to Use Dental Care by Industrial Workers Due to COVID-19: Application of Anderson Model and Planned Behavior Theory
- PMID: 36232183
- PMCID: PMC9564458
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph191912883
Factors Related to the Intention to Use Dental Care by Industrial Workers Due to COVID-19: Application of Anderson Model and Planned Behavior Theory
Abstract
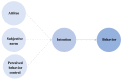
The COVID-19 pandemic has affected medical and dental care in Korea. This study aimed to investigate the factors influencing the intention to use dental care in industrial workers, an economically active population. An online questionnaire survey was completed by 301 industrial workers. Stress and anxiety to viral epidemics-6 (SAVE-6), attitude, subjective norm, perceived behavior control, and intention to use dental care, based on the theory of planned behavior (TPB), were measured. Predisposing, enabling, and need factors based on the Andersen model were measured as control variables for influencing factors. In the final hierarchical multiple regression analysis, the most significant relevant factors affecting intention to use dental care were attitude (β = 0.598, p < 0.001), followed by experience of dental clinic visits (β = 0.237, p < 0.001), subjective norm (β = 0.125, p < 0.001), perceived behavior control (β = 0.114, p = 0.004), SAVE-6 (β = -0.073, p = 0.025), and gingival bleeding (β = 0.062, p = 0.029). Dental care use decreased to 58.5%, and socio-psychological factors based on TPB were closely associated with the intention to use dental care. Therefore, awareness must be raised regarding oral health practices to increase the use of dental care among industrial workers.
Keywords: COVID-19; anxiety; dental care; intention; stress; workers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predicting Intention to Take a COVID-19 Vaccine in the United States: Application and Extension of Theory of Planned Behavior.Am J Health Promot. 2022 May;36(4):710-713. doi: 10.1177/08901171211062584. Epub 2022 Jan 18. Am J Health Promot. 2022. PMID: 35041541 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting intention of Norwegian dental health-care workers to use nanomaterials: An application of the augmented theory of planned behavior.Eur J Oral Sci. 2021 Dec;129(6):e12821. doi: 10.1111/eos.12821. Epub 2021 Nov 2. Eur J Oral Sci. 2021. PMID: 34729822
-
Predicting Pharmacist Intention to Contribute to COVID-19 Management at the Community Level: A Cross-Sectional Survey Study.Front Public Health. 2021 Jul 22;9:653335. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.653335. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34368042 Free PMC article.
-
Factors influencing implementation of personalized prevention plans among annual wellness visit patients using the theory of planned behavior: A quantitative study.Res Social Adm Pharm. 2021 Sep;17(9):1636-1644. doi: 10.1016/j.sapharm.2021.01.002. Epub 2021 Jan 18. Res Social Adm Pharm. 2021. PMID: 33678585
-
Factors Influencing Intention to Work while Ill: A Systematic Review.Am J Health Behav. 2021 Nov 15;45(6):1016-1030. doi: 10.5993/AJHB.45.6.6. Am J Health Behav. 2021. PMID: 34969413
References
-
- Ministry of Health and Welfare Dental Infection Control Standard Policy & Procedure; Sejong, Korea. 2020. [(accessed on 15 September 2021)]. Available online: http://www.mohw.go.kr/react/jb/sjb030301vw.jsp?PAR_MENU_ID=03&MENU_ID=03....
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Pandemic. [(accessed on 15 September 2021)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019.
-
- National Assembly Budget Office (NABO) Changes in Health Insurance Care Costs and Implications before and after COVID-19. [(accessed on 28 October 2020)]. Available online: https://nabo.go.kr/
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical