Psychophysiological and Metabolomics Responses of Adults during Horticultural Activities Using Soil Inoculated with Streptomyces rimosus: A Pilot Study
- PMID: 36232200
- PMCID: PMC9564959
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph191912901
Psychophysiological and Metabolomics Responses of Adults during Horticultural Activities Using Soil Inoculated with Streptomyces rimosus: A Pilot Study
Abstract
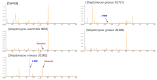
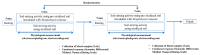
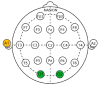
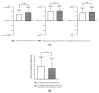
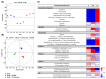
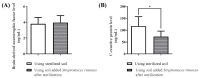
This study compared the physiological effects at a metabolomics level with autonomic nervous system responses in adults during soil mixing activities, based on the presence or absence of Streptomyces rimosus in the soil. Thirty adult participants performed soil mixing activities for 5 min using sterilized soil with culture media and Streptomyces rimosus, respectively. Blood samples were drawn twice from each participant after each activity. Electroencephalograms were measured during the activity. Serum metabolites underwent metabolite profiling by gas chromatography, followed by multivariate analyses. Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor and C-reactive protein levels were measured by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay. Soil-emitted volatile organic compounds were identified via solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography-mass spectroscopy, followed by multivariate analyses. The volatile compound analysis revealed that the terpenoid and benzoid compounds, geosmin, and 2-methylisoborneol were greater in soil with Streptomyces rimosus. Serum metabolomics revealed that the treatment group (soil inoculated with Streptomyces rimosus) possessed relatively higher levels of serotonin compared to the control group (soil mixed with culture media), and serum C-reactive protein levels were significantly lower in the treatment group. In the treatment group, the electroencephalogram revealed that alpha band activity of the occipital lobe increased. This study concludes that Streptomyces rimosus soil contact can positively affect human metabolic and autonomic reactions. Therefore, this pilot study confirmed the possible role of soil microorganisms in horticultural activities for psychophysiological effects in humans.
Keywords: 2-methylisoborneol; C-reactive protein; brain-derived neurotrophic factor; electroencephalogram; gardening; geosmin; horticultural therapy; metabolite profiling; soil microorganism; volatile compounds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflict of interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Psychophysiological Responses of Humans during Seed-Sowing Activity Using Soil Inoculated with Streptomyces rimosus.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Dec 5;19(23):16275. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192316275. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36498346 Free PMC article.
-
Horticultural activity in soil inoculated with Streptomyces rimosus improved depressive mood with altered electroencephalogram and serum metabolism in adults.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 16;15(1):2197. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79159-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39820093 Free PMC article.
-
[Purification and chemical characterization of antimicrobial compounds from a new soil isolate Streptomyces rimosus MTCC 10792].Prikl Biokhim Mikrobiol. 2013 Sep-Oct;49(5):467-75. Prikl Biokhim Mikrobiol. 2013. PMID: 25474869 Russian.
-
Antifungal activity change of Streptomyces rimosus MY02 mediated by confront culture with other microorganism.J Basic Microbiol. 2017 Mar;57(3):276-282. doi: 10.1002/jobm.201600498. Epub 2017 Feb 17. J Basic Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28211942
-
Enhanced Oxytetracycline Production by Streptomyces rimosus in Submerged Co-Cultures with Streptomyces noursei.Molecules. 2021 Oct 5;26(19):6036. doi: 10.3390/molecules26196036. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34641580 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Psychophysiological Responses of Humans during Seed-Sowing Activity Using Soil Inoculated with Streptomyces rimosus.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Dec 5;19(23):16275. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192316275. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36498346 Free PMC article.
-
Horticultural activity in soil inoculated with Streptomyces rimosus improved depressive mood with altered electroencephalogram and serum metabolism in adults.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 16;15(1):2197. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79159-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39820093 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kim M., Sowndhararajan K., Kim T., Kim J.E., Yang J.E., Kim S. Gender differences in electroencephalographic activity in response to the earthy odorants geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol. Appl. Sci. 2017;7:876. doi: 10.3390/app7090876. - DOI
-
- Haese G., Humeau P., De Oliveira F., Le Callet P., Le Cloirec P. Tastes and odors of water—Quantifying objective analyses: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014;44:2455–2501. doi: 10.1080/10643389.2013.829972. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

